

法医学杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 211-216.DOI: 10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2023.430407
• 案例报道 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-04-14
发布日期:2024-06-07
出版日期:2024-04-25
通讯作者:
乔东访
作者简介:景嘉钰(2002—),女,主要从事法医病理学研究;E-mail:jingjiayuu@foxmail.com
Received:2023-04-14
Online:2024-06-07
Published:2024-04-25
中图分类号:
景嘉钰, 徐璐瑶, 杜思昊, 岳霞, 乔东访. 宏基因组测序辅助鉴定输液致血流感染死亡1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(2): 211-216.
| 样本 | 检出的病原体 |
|---|---|
| 尿道口拭子 | E. bugandensis、阴道加德纳菌、咽峡炎链球菌 |
| 腋窝拭子 | 棒状杆菌属菌、表皮葡萄球菌 |
| 扁桃体 | 中间链球菌 |
| 肺 | - |
| 小肠 | 粪肠球菌 |
| 膀胱 | E. bugandensis、粪肠球菌 |
| 左手背皮下软组织 | - |
| 右手背皮下软组织 | - |
| 血液 | E. bugandensis |
| 复方氨基酸注射液 | E. bugandensis |
| 氯化钠溶液 | - |
表1 各样本中病原体的mNGS检测结果
Tab. 1 mNGS detection results ofpathogens in each sample
| 样本 | 检出的病原体 |
|---|---|
| 尿道口拭子 | E. bugandensis、阴道加德纳菌、咽峡炎链球菌 |
| 腋窝拭子 | 棒状杆菌属菌、表皮葡萄球菌 |
| 扁桃体 | 中间链球菌 |
| 肺 | - |
| 小肠 | 粪肠球菌 |
| 膀胱 | E. bugandensis、粪肠球菌 |
| 左手背皮下软组织 | - |
| 右手背皮下软组织 | - |
| 血液 | E. bugandensis |
| 复方氨基酸注射液 | E. bugandensis |
| 氯化钠溶液 | - |
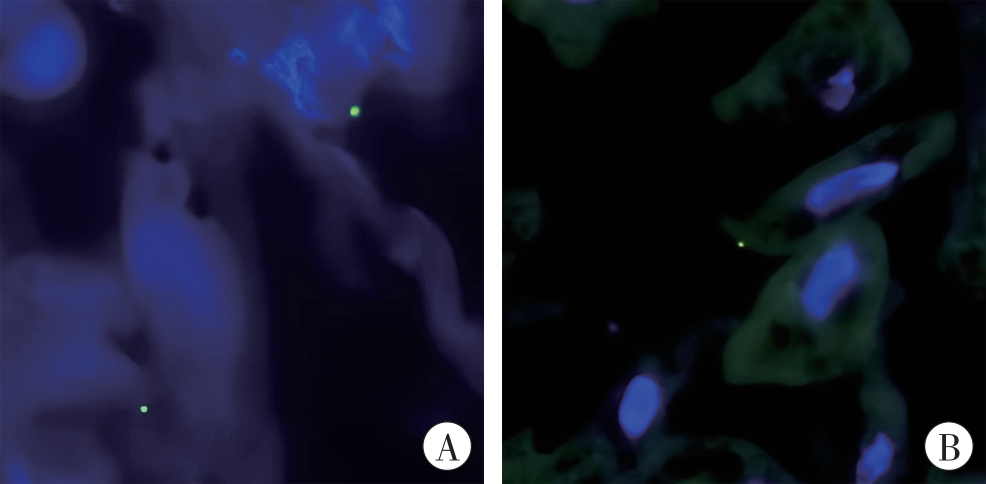
图4 脾和肝组织中的E. bugandensis(FISH检测,1 000×)A:脾;B:肝。绿色荧光显示FITC荧光染料标记的细菌位置,蓝色荧光显示DAPI荧光染料标记的细胞核。
Fig. 4 E. bugandensis in spleen and liver tissues(detected by FISH, 1 000×)
| 1 | PRUDENT E, RAOULT D. Fluorescence in situ hybridization, a complementary molecular tool for the clinical diagnosis of infectious diseases by intracellular and fastidious bacteria[J]. FEMS Microbiol Rev,2019,43(1):88-107. doi:10.1093/femsre/fuy040 . |
| 2 | SINGER M, DEUTSCHMAN C S, SEYMOUR C W, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA,2016,315(8):801-810. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.0287 . |
| 3 | RUDD K E, JOHNSON S C, AGESA K M, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990—2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study[J]. Lancet,2020,395(10219):200-211. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7 . |
| 4 | PETSCH D, ANSPACH F B. Endotoxin removal from protein solutions[J]. J Biotechnol,2000,76(2/3):97-119. doi:10.1016/s0168-1656(99)00185-6 . |
| 5 | ŚMIECHOWICZ J. The rationale and current status of endotoxin adsorption in the treatment of septic shock[J]. J Clin Med,2022,11(3):619. doi:10.3390/jcm11030619 . |
| 6 | TANI V M, ASSIS-MENDONÇA G R, SILVA T B DA, et al. Microvascular thrombosis in sepsis: An autopsy study[J]. Thromb Res,2017,156:23-25. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2017.05.031 . |
| 7 | YANG Y, XIE J, GUO F, et al. Combination of C-reactive protein, procalcitonin and sepsis-related organ failure score for the diagnosis of sepsis in critical patients[J]. Ann Intensive Care,2016,6(1):51. doi:10.1186/s13613-016-0153-5 . |
| 8 | MSHANA S E, GERWING L, MINDE M, et al. Outbreak of a novel Enterobacter sp. carrying blaCTX-M-15 in a neonatal unit of a tertiary care hospital in Tanzania[J]. Int J Antimicrob Agents,2011,38(3):265-269. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.05.009 . |
| 9 | FALGENHAUER J, IMIRZALIOGLU C, FAL-GENHAUER L, et al. Whole-genome sequences of clinical Enterobacter bugandensis isolates from Germany[J]. Microbiol Resour Announc,2019,8(29):e00465-e00419. doi:10.1128/MRA.00465-19 . |
| 10 | PATI N B, DOIJAD S P, SCHULTZE T, et al. Enterobacter bugandensis: A novel enterobacterial species associated with severe clinical infection[J]. Sci Rep,2018,8(1):5392. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-23069-z . |
| 11 | SALLEM R BEN, ARFAOUI A, NAJJARI A, et al. First report of IMI-2-producing Enterobacter bugandensis and CTX-M-55-producing Escherichia coli isolated from healthy volunteers in Tunisia[J]. Antibiotics (Basel),2023,12(1):116. doi:10.3390/antibiotics12010116 . |
| 12 | GU W, MILLER S, CHIU C Y. Clinical metagenomic next-generation sequencing for pathogen detection[J]. Annu Rev Pathol,2019,14:319-338. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012751 . |
| 13 | CALISTRI A, PALÙ G. Editorial commentary: Unbiased next-generation sequencing and new pathogen discovery: Undeniable advantages and still-existing drawbacks[J]. Clin Infect Dis,2015,60(6):889-891. doi:10.1093/cid/ciu913 . |
| 14 | GRUMAZ C, HOFFMANN A, VAINSHTEIN Y, et al. Rapid next-generation sequencing-based diagnostics of bacteremia in septic patients[J]. J Mol Diagn,2020,22(3):405-418. doi:10.1016/j.jmoldx.2019.12.006 . |
| 15 | LONG Y, ZHANG Y, GONG Y, et al. Diagnosis of sepsis with cell-free DNA by next-generation sequencing technology in ICU patients[J]. Arch Med Res,2016,47(5):365-371. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2016.08.004 . |
| 16 | SHERIDAN C. COVID-19 spurs wave of innovative diagnostics[J]. Nat Biotechnol,2020,38(7):769-772. doi:10.1038/s41587-020-0597-x . |
| 17 | KUIPER I. Microbial forensics: Next-generation sequencing as catalyst: The use of new sequencing technologies to analyze whole microbial communities could become a powerful tool for forensic and criminal investigations[J]. EMBO Rep,2016,17(8):1085-1087. doi:10.15252/embr.201642794 . |
| 18 | SCHMEDES S E, SAJANTILA A, BUDOWLE B. Expansion of microbial forensics[J]. J Clin Microbiol,2016,54(8):1964-1974. doi:10.1128/JCM.00046-16 . |
| 19 | YU Z, XIE Q, ZHAO Y, et al. NGS plus bacterial culture: A more accurate method for diagnosing forensic-related nosocomial infections[J]. Leg Med (Tokyo),2021,52:101910. doi:10.1016/j.legalmed.2021.101910 . |
| 20 | GUO J, FU X, LIAO H, et al. Potential use of bacterial community succession for estimating post-mortem interval as revealed by high-throughput sequencing[J]. Sci Rep,2016,6:24197. doi:10.1038/srep24197 . |
| 21 | HYDE E R, HAARMANN D P, LYNNE A M, et al. The living dead: Bacterial community structure of a cadaver at the onset and end of the bloat stage of decomposition[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(10):e77733. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077733 . |
| 22 | RIEDEL S. The value of postmortem microbiology cultures[J]. J Clin Microbiol,2014,52(4):1028-1033. doi:10.1128/JCM.03102-13 . |
| 23 | SIMNER P J, MILLER S, CARROLL K C. Understanding the promises and hurdles of metagenomic next-generation sequencing as a diagnostic tool for infectious diseases[J]. Clin Infect Dis,2018,66(5):778-788. doi:10.1093/cid/cix881 . |
| 24 | GOSIEWSKI T, LUDWIG-GALEZOWSKA A H, HUMINSKA K, et al. Comprehensive detection and identification of bacterial DNA in the blood of patients with sepsis and healthy volunteers using next-generation sequencing method — The observation of DNAemia[J]. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis,2017,36(2):329-336. doi:10.1007/s10096-016-2805-7 . |
| 25 | 中华医学会检验医学分会临床微生物学组,中华医学会微生物学与免疫学分会临床微生物学组,中国医疗保健国际交流促进会临床微生物与感染分会. 宏基因组高通量测序技术应用于感染性疾病病原检测中国专家共识[J].中华检验医学杂志,2021,44(2):107-120. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn114452-20201026-00794 . |
| Clinical Microbiology Group of Chinese Society of Laboratory Medicine, Clinical Microbiology Group of Chinese Society of Microbiology and Immunology, Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infection of China International Exchange and Promotion Association for Medical and Healthcare. Chinese expert consensus on metagenomics next-generation sequencing application on pathogen detection of infectious diseases[J]. Zhonghua Jianyan Yixue Zazhi,2021,44(2):107-120. | |
| 26 | 宏基因组学测序技术在中重症感染中的临床应用共识专家组,中国研究型医院学会脓毒症与休克专业委员会,中国微生物学会微生物毒素专业委员会,等. 宏基因组学测序技术在中重症感染中的临床应用专家共识(第一版)[J].中华危重病急救医学,2020,32(5):531-536. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200228-00095 . |
| Consensus Group of Experts on Application of Metagenomic Next Generation Sequencing in the Pathogen Diagnosis in Clinical Moderate and Severe Infections, Professional Committee of Sepsis and Shock, Chinese Research Hospital Association, Professional Committee of Microbial Toxins, Chinese Society for Microbiology, et al. Expert consensus for the application of metagenomic next generation sequencing in the pathogen diagnosis in clinical moderate and severe infections (first edition)[J]. Zhonghua Weizhongbing Jijiu Yixue,2020,32(5):531-536. | |
| 27 | 中华医学会检验医学分会. 高通量宏基因组测序技术检测病原微生物的临床应用规范化专家共识[J].中华检验医学杂志,2020,43(12):1181-1195. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn114452-20200903-00704 . |
| Chinese Society of Laboratory Medicine. Expert consensus on clinical standardized application of metagenomics next-generation sequencing for detection of pathogenic microorganisms[J]. Zhonghua Jianyan Yi-xue Zazhi,2020,43(12):1181-1195. | |
| 28 | MALLA M A, DUBEY A, KUMAR A, et al. Exploring the human microbiome: The potential future role of next-generation sequencing in disease diagnosis and treatment[J]. Front Immunol,2018,9:2868. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02868 . |
| [1] | 陈光, 王小龙, 项慧敏, 汪露, 秦明, 刘岫, 徐祥. 虚拟解剖结合法医学尸体检验判定气枪弹创致死1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(2): 196-199. |
| [2] | 宋旦, 单华鑫, 王福远, 李正东. 压缩式垃圾车挤压致死1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(2): 205-207. |
| [3] | 王悦, 刘希, 李广云, 刘明哲, 陈新山. 腹股沟疝修补术中恶性高热死亡法医学鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(2): 208-210. |
| [4] | 黄武林, 李玲玉, 彭建伟, 邹梦琴, 章青波. 毒性弥漫性甲状腺肿并发脑梗死法医学鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(2): 199-201. |
| [5] | 陈尚亨, 董盛仲, 王智敏, 洪光辉, 叶星, 林子杰, 林俊毅, 江洁清, 王守宇, 林汉成, 沈忆文. 束缚应激致高脂血症ApoE-/-小鼠心肌损伤的分子靶标筛选与机制分析[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(2): 172-178. |
| [6] | 吴娟娟, 黄俊杰, 张煜, 卓嘉英, 陈刚, 杨舒涵, 赵蕴琦, 范琰琰. IL-10、TGF-β1在小鼠深静脉血栓中的时序性变化[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(2): 179-185. |
| [7] | 徐杰, 薛晓明, 王玉宝, 岳宇, 张阳. 结合现场环境及植物物证推断死亡时间1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(2): 202-204. |
| [8] | 徐碧宇, 吴晨阳, 姬艳琦, 李莹莹, 宋旭东. 二叶主动脉瓣伴动脉夹层破裂1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 77-79. |
| [9] | 周杰, 邹亚晶, 姚建. 开放场所性窒息法医学鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 86-87. |
| [10] | 邢运虹, 李洋, 王文政, 王亮亮, 孙乐乐, 杜秋香, 曹洁, 何光龙, 孙俊红. 不稳定冠状动脉粥样斑块病理特征及分类[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 59-63. |
| [11] | 靳茜茜, 白雅琴, 陈念念, 董祎铭, 高学慧, 孙修强, 王君丽, 曹洁, 梁新华, 郭相杰. 癫痫持续状态死亡法医学鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 83-85. |
| [12] | 杜琳, 郭兵兵, 叶才极, 陶欢, 杨小凤, 龚道银. 过敏性紫癜致心脏损害累及传导系统死亡1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 80-82. |
| [13] | 云鹏, 陈安琪, 陈丽琴, 李成涛. 42个微单倍型复合检测体系的构建及法医学应用[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 50-58. |
| [14] | 曾达, 郑杏斌. 腹腔镜胃癌根治术后十二指肠残端漏死亡医疗损害鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 88-92. |
| [15] | 朱玮玮, 杨晨光, 潘美辰, 孙天迎, 刘慧讷, 董红梅. 胸主动脉穿透性动脉粥样硬化性溃疡破裂死亡1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(6): 617-619. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
