

法医学杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 20-29.DOI: 10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2022.521010
范庆炜1,2( ), 李凌1, 杨慧凌1, 邓婷婷2, 徐冬冬1, 王韵1, 杜冰1,2(
), 李凌1, 杨慧凌1, 邓婷婷2, 徐冬冬1, 王韵1, 杜冰1,2( ), 严江伟3(
), 严江伟3( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-31
发布日期:2024-03-19
出版日期:2024-02-25
通讯作者:
杜冰,严江伟
作者简介:范庆炜(1992—),男,硕士研究生,助教,主要从事法医遗传学及文献计量学研究;E-mail:fqw1720@163.com
基金资助:
Qing-wei FAN1,2( ), Ling LI1, Hui-ling YANG1, Ting-ting DENG2, Dong-dong XU1, Yun WANG1, Bing DU1,2(
), Ling LI1, Hui-ling YANG1, Ting-ting DENG2, Dong-dong XU1, Yun WANG1, Bing DU1,2( ), Jiang-wei YAN3(
), Jiang-wei YAN3( )
)
Received:2022-10-31
Online:2024-03-19
Published:2024-02-25
Contact:
Bing DU, Jiang-wei YAN
摘要:
目的 通过文献计量学方法,探明法医学混合斑研究的脉络与热点变化。 方法 以2011—2022年Web of Science数据库核心合集所收录的法医学混合斑文献为研究对象,利用基于R语言Bibliometrix 1.1.6包和VOSviewer 1.6.18软件对年发文量、国家(地区)、机构、期刊、关键词等方面进行文献计量和可视化分析。 结果 2011—2022年共纳入732篇法医学混合斑研究的文献,年发文量及年被引频次总体展现逐年平稳上升的趋势。59个发文国家(地区)中最多为美国246篇,其次为中国153篇;文献来源于104本期刊,发文量前10的期刊上发文总数为633篇,FORENSIC SCI INT GENET发文量为307篇,排名第1;利用VOSviewer软件可视化分析显示,关键词可被区分为4个研究聚类,分别为遗传标记发展组(蓝色)、混合斑分型分析理论组(红色)、测序分析组(黄色)、案件样本研究组(绿色);从不同时段上可分为发展早期(2011—2013年)、发展中期(2014—2016年)、快速发展期(2017—2020年)、最新发展期(2021—2022年)4个发展阶段。 结论 国内外学者在法医学混合斑研究的发文量呈现较为平稳的趋势,机器学习、下一代测序等研究是近年来最受关注的热点主题,有望使法医学混合斑研究在混合斑分型分析理论和测序分析研究等方面得到更进一步的发展。
中图分类号:
范庆炜, 李凌, 杨慧凌, 邓婷婷, 徐冬冬, 王韵, 杜冰, 严江伟. 法医学混合斑研究现状及趋势的文献计量和可视化分析[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 20-29.
Qing-wei FAN, Ling LI, Hui-ling YANG, Ting-ting DENG, Dong-dong XU, Yun WANG, Bing DU, Jiang-wei YAN. A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis of the Current Status and Trends of Forensic Mixed Stain Research[J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2024, 40(1): 20-29.
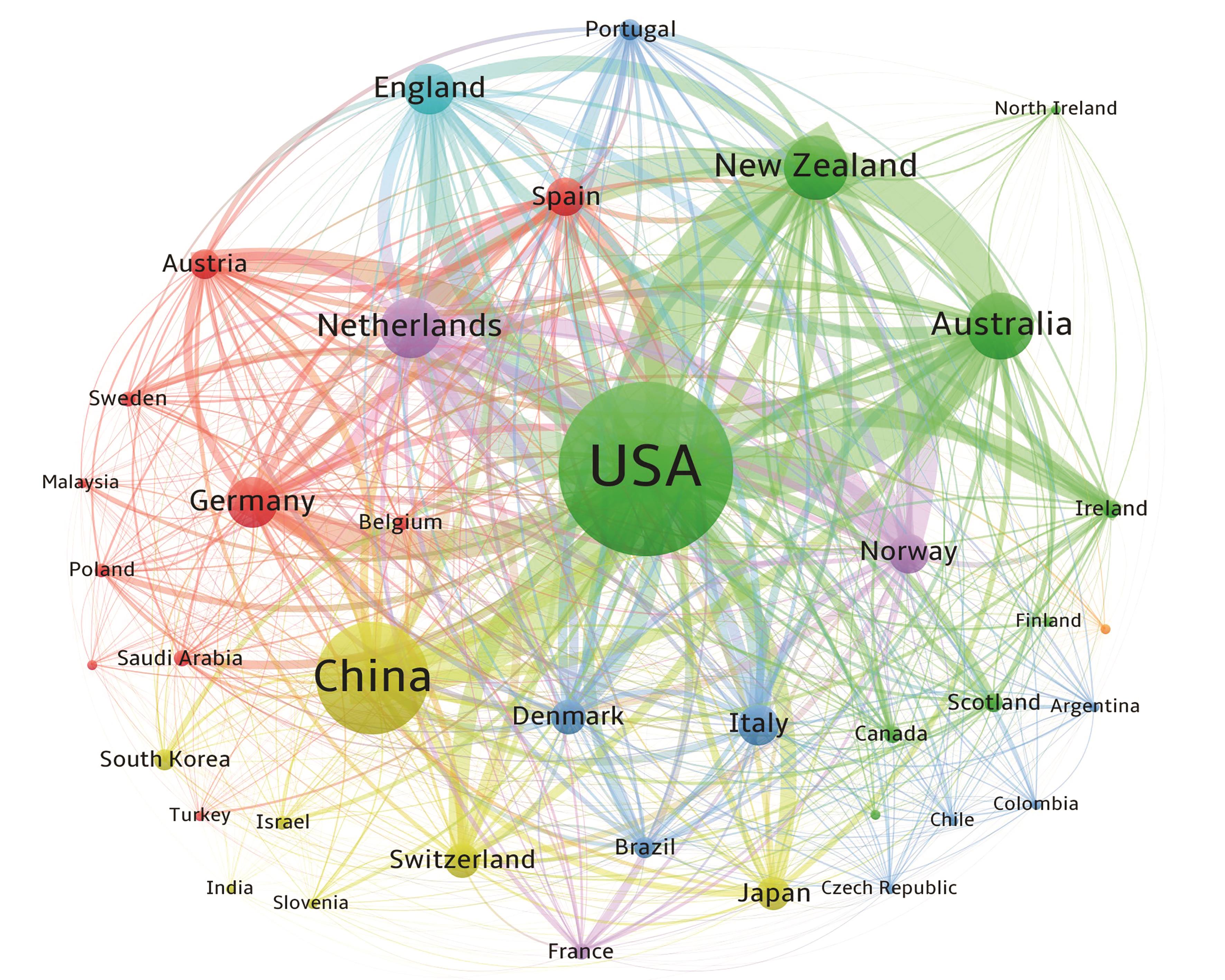
图2 法医学混合斑领域国家(地区)共现网络图谱以发文量≥3篇对共现网络进行剪枝,节点越大表示发文量越高,连线越粗表示关联强度越紧密,具有相同颜色的节点表示同一个聚类。
Fig. 2 Co-occurrence network mapping for countries (regions) in the field of forensic mixed stain
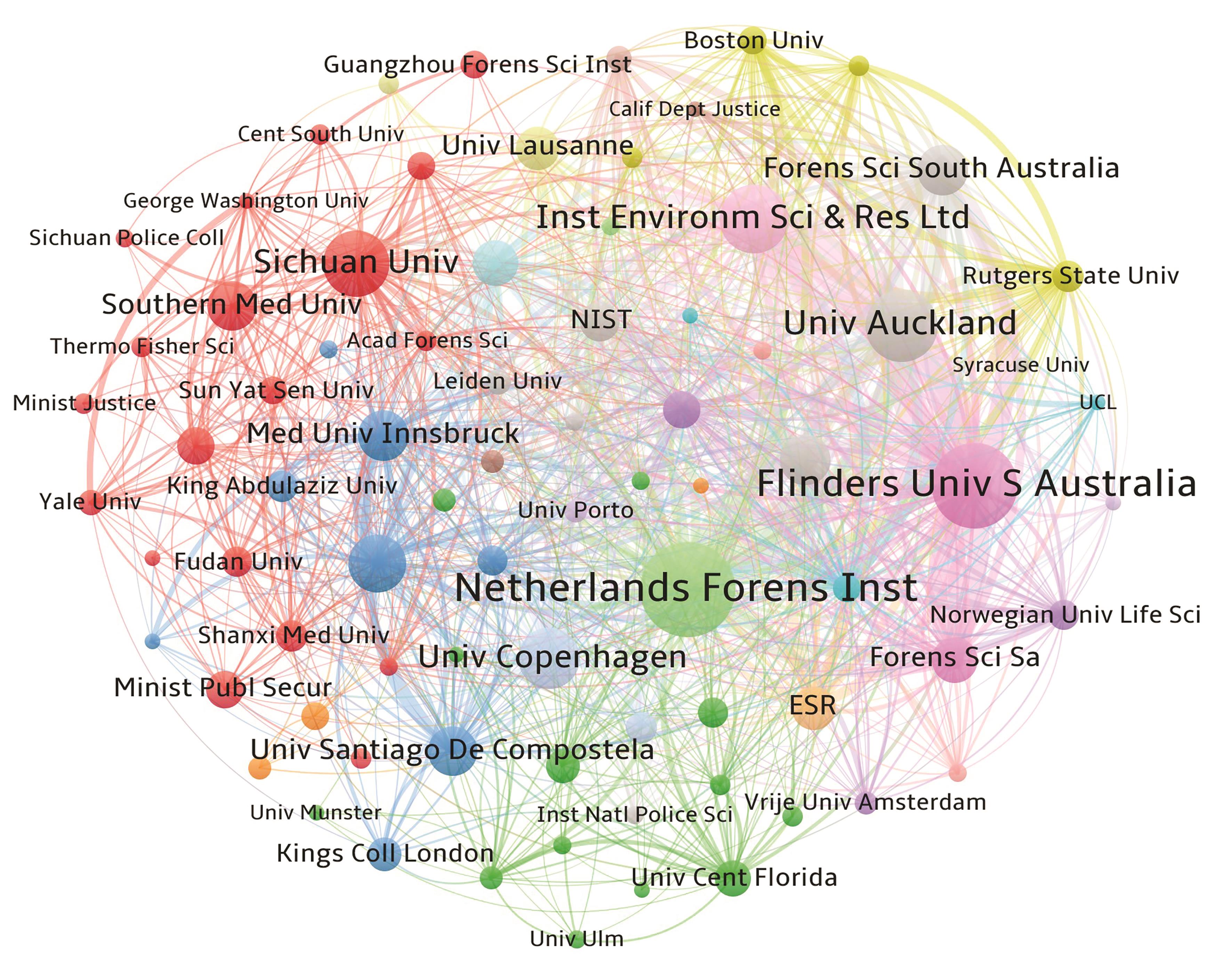
图3 法医学混合斑领域机构共现网络图谱以发文量≥3篇对共现网络进行剪枝,节点越大表示发文量越高,连线越粗表示关联强度越紧密,具有相同颜色的节点表示同一个聚类。
Fig. 3 Co-occurrence network mapping for institutions in the field of forensic mixed stain
| 期刊全称 | 期刊缩写 | 发文量/篇 | 影响因子 | 分区 | 国家 | 被引频次 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forensic Science International-Genetics | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | 306 | 4.453 | Q1 | 爱尔兰 | 7 699 |
| International Journal of Legal Medicine | INT J LEGAL MED | 87 | 2.791 | Q1 | 德国 | 846 |
| Journal of Forensic Sciences | J FORENSIC SCI | 45 | 1.717 | Q3 | 美国 | 703 |
| Electrophoresis | ELECTROPHORESIS | 39 | 3.595 | Q2 | 德国 | 463 |
| Legal Medicine | LEGAL MED-TOKYO | 26 | 2.017 | Q3 | 美国 | 144 |
| Forensic Science International | FORENSIC SCI INT | 23 | 2.676 | Q2 | 爱尔兰 | 151 |
| Science & Justice | SCI JUSTICE | 23 | 1.993 | Q3 | 英国 | 439 |
| Genes | GENES | 16 | 4.141 | Q2 | 瑞士 | 94 |
| PLoS One | PLOS ONE | 14 | 3.752 | Q2 | 美国 | 294 |
| Australian Journal of Forensic Sciences | AUS J FORENSIC SCI | 13 | 1.210 | Q4 | 英国 | 29 |
表1 法医学混合斑研究发文量前10的期刊
Tab. 1 Top 10 journals publishing articles in forensic mixed stain research
| 期刊全称 | 期刊缩写 | 发文量/篇 | 影响因子 | 分区 | 国家 | 被引频次 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forensic Science International-Genetics | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | 306 | 4.453 | Q1 | 爱尔兰 | 7 699 |
| International Journal of Legal Medicine | INT J LEGAL MED | 87 | 2.791 | Q1 | 德国 | 846 |
| Journal of Forensic Sciences | J FORENSIC SCI | 45 | 1.717 | Q3 | 美国 | 703 |
| Electrophoresis | ELECTROPHORESIS | 39 | 3.595 | Q2 | 德国 | 463 |
| Legal Medicine | LEGAL MED-TOKYO | 26 | 2.017 | Q3 | 美国 | 144 |
| Forensic Science International | FORENSIC SCI INT | 23 | 2.676 | Q2 | 爱尔兰 | 151 |
| Science & Justice | SCI JUSTICE | 23 | 1.993 | Q3 | 英国 | 439 |
| Genes | GENES | 16 | 4.141 | Q2 | 瑞士 | 94 |
| PLoS One | PLOS ONE | 14 | 3.752 | Q2 | 美国 | 294 |
| Australian Journal of Forensic Sciences | AUS J FORENSIC SCI | 13 | 1.210 | Q4 | 英国 | 29 |
| 序号 | 作者 | 期刊 | 文题 | 年份 | LC/次 | GC/次 | LC/GC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Perlin MW | J FORENSIC SCI | Validating TrueAllele® DNA Mixture Interpretation[ | 2011 | 98 | 152 | 0.644 7 |
| 2 | Taylor D | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | The interpretation of single source and mixed DNA profiles[ | 2013 | 88 | 170 | 0.517 6 |
| 3 | Bleka O | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | EuroForMix: An open source software based on a continuous model to evaluate STR DNA profiles from a mixture of contributors with artefacts[ | 2016 | 80 | 142 | 0.563 4 |
| 4 | Gill P | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | DNA commission of the International Society of Forensic Genetics: Recommendations on the evaluation of STR typing results that may include drop-out and/or drop-in using probabilistic methods[ | 2012 | 58 | 121 | 0.479 3 |
| 5 | Bright JA | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | Developing allelic and stutter peak height models for a continuous method of DNA interpretation[ | 2013 | 56 | 102 | 0.549 0 |
| 6 | Gill P | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | A new methodological framework to interpret complex DNA profiles using likelihood ratios[ | 2013 | 51 | 87 | 0.586 2 |
| 7 | Bright JA | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | Developmental validation of STRmixTM, expert software for the interpretation of forensic DNA profiles[ | 2016 | 50 | 73 | 0.684 9 |
| 8 | Cowell RG | J R STAT SOC C-APPL | Analysis of forensic DNA mixtures with artefacts[ | 2015 | 41 | 69 | 0.594 2 |
| 9 | Børsting C | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | Next generation sequencing and its applications in forensic genetics[ | 2015 | 41 | 230 | 0.178 3 |
| 10 | Haned H | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | Exploratory data analysis for the interpretation of low template DNA mixtures[ | 2012 | 40 | 67 | 0.597 0 |
表2 法医学混合斑领域前10被引文献
Tab. 2 Top 10 highly cited publications in the field of forensic mixed stain
| 序号 | 作者 | 期刊 | 文题 | 年份 | LC/次 | GC/次 | LC/GC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Perlin MW | J FORENSIC SCI | Validating TrueAllele® DNA Mixture Interpretation[ | 2011 | 98 | 152 | 0.644 7 |
| 2 | Taylor D | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | The interpretation of single source and mixed DNA profiles[ | 2013 | 88 | 170 | 0.517 6 |
| 3 | Bleka O | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | EuroForMix: An open source software based on a continuous model to evaluate STR DNA profiles from a mixture of contributors with artefacts[ | 2016 | 80 | 142 | 0.563 4 |
| 4 | Gill P | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | DNA commission of the International Society of Forensic Genetics: Recommendations on the evaluation of STR typing results that may include drop-out and/or drop-in using probabilistic methods[ | 2012 | 58 | 121 | 0.479 3 |
| 5 | Bright JA | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | Developing allelic and stutter peak height models for a continuous method of DNA interpretation[ | 2013 | 56 | 102 | 0.549 0 |
| 6 | Gill P | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | A new methodological framework to interpret complex DNA profiles using likelihood ratios[ | 2013 | 51 | 87 | 0.586 2 |
| 7 | Bright JA | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | Developmental validation of STRmixTM, expert software for the interpretation of forensic DNA profiles[ | 2016 | 50 | 73 | 0.684 9 |
| 8 | Cowell RG | J R STAT SOC C-APPL | Analysis of forensic DNA mixtures with artefacts[ | 2015 | 41 | 69 | 0.594 2 |
| 9 | Børsting C | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | Next generation sequencing and its applications in forensic genetics[ | 2015 | 41 | 230 | 0.178 3 |
| 10 | Haned H | FORENSIC SCI INT GENET | Exploratory data analysis for the interpretation of low template DNA mixtures[ | 2012 | 40 | 67 | 0.597 0 |
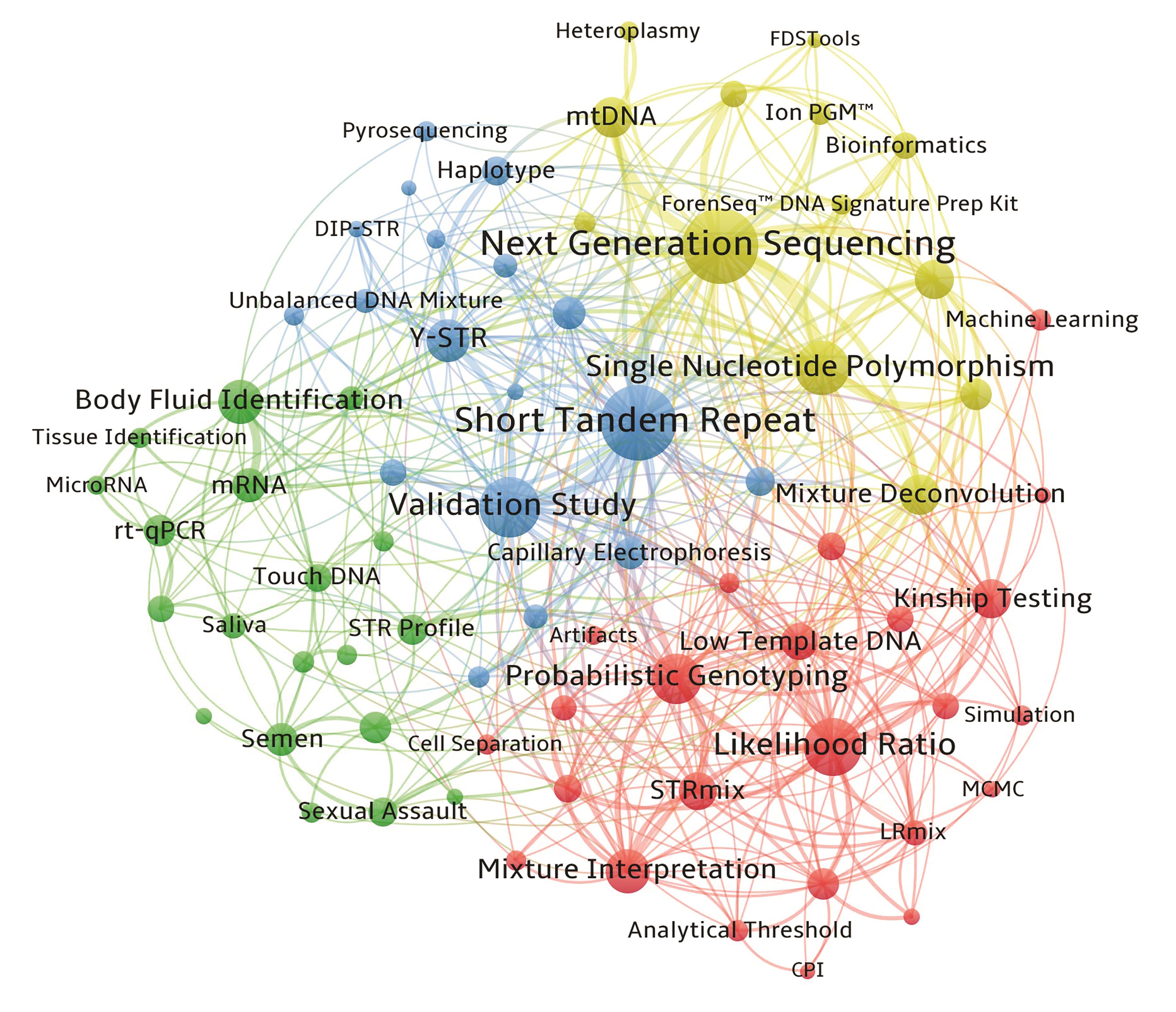
图5 关键词共现网络图谱以关键词频次≥5次对共现网络进行剪枝,节点越大反映关键词出现的频次越高,节点间的连线代表相互间的共现关系,连线越粗代表了关键词的关联强度越紧密,同一种颜色的节点标识可同属一个聚类。
Fig. 5 Co-occurrence network mapping for keywords
| 1 | ARIA M, CUCCURULLO C. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis[J]. J Informetrics,2017,11(4):959-975. doi:10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007 . |
| 2 | VAN ECK N J, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping[J]. Scientometrics, 2010,84(2):523-538. doi:10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3 . |
| 3 | PERLIN M W, LEGLER M M, SPENCER C E, et al. Validating TrueAllele® DNA mixture interpretation[J]. J Forensic Sci,2011,56(6):1430-1447. doi:10.1111/j.1556-4029.2011.01859.x . |
| 4 | TAYLOR D, BRIGHT J A, BUCKLETON J. The interpretation of single source and mixed DNA profiles[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2013,7(5):516-528. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2013.05.011 . |
| 5 | BLEKA Ø, STORVIK G, GILL P. EuroForMix: An open source software based on a continuous model to evaluate STR DNA profiles from a mixture of contributors with artefacts[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2016,21:35-44. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen. 2015.11.008 . |
| 6 | GILL P, GUSMÃO L, HANED H, et al. DNA commission of the International Society of Forensic Genetics: Recommendations on the evaluation of STR typing results that may include drop-out and/or drop-in using probabilistic methods[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2012,6(6):679-688. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2012.06.002 . |
| 7 | BRIGHT J A, TAYLOR D, CURRAN J M, et al. Developing allelic and stutter peak height models for a continuous method of DNA interpretation[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2013,7(2):296-304. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2012.11.013 . |
| 8 | GILL P, HANED H. A new methodological framework to interpret complex DNA profiles using likelihood ratios[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2013,7(2):251-263. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2012.11.002 . |
| 9 | BRIGHT J A, TAYLOR D, MCGOVERN C, et al. Developmental validation of STRmixTM, expert software for the interpretation of forensic DNA profiles[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2016,23:226-239. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.20 16.05.007 . |
| 10 | COWELL R G, GRAVERSEN T, LAURITZEN S L, et al. Analysis of forensic DNA mixtures with artefacts[J]. J R Stat Soc Series B Appl Stat,2015,64(1):1-48. doi:10.1111/rssc.12071 . |
| 11 | BØRSTING C, MORLING N. Next generation sequencing and its applications in forensic genetics[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2015,18:78-89. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2015.02.002 . |
| 12 | HANED H, SLOOTEN K, GILL P. Exploratory data analysis for the interpretation of low template DNA mixtures[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2012,6(6):762-774. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2012.08.008 . |
| 13 | ZHANG J S, ZHANG J Y, TAO R Y, et al. A newly devised multiplex assay of novel polymorphic non-CODIS STRs as a valuable tool for forensic application [J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2020, 48: 8. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2020.102341 . |
| 14 | WANG Z, ZHOU D, WANG H, et al. Massively parallel sequencing of 32 forensic markers using the Precision ID GlobalFilerTM NGS STR Panel and the Ion PGMTM System[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2017,31:126-34. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2017. 09.004 . |
| 15 | MANABE S, FUJII K, FUKAGAWA T, et al. Evaluation of probability distribution models for stutter ratios in the typing system of GlobalFiler and 3500xL Genetic Analyzer[J]. Legal Med,2021,52:101906. doi:10.1016/j.legalmed.2021.101906 . |
| 16 | ALGHAFRI R, GOODWIN W, RALF A, et al. A novel multiplex assay for simultaneously analysing 13 rapidly mutating Y-STRs[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2015,17:91-98. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2015. 04.004 . |
| 17 | ANDERSEN M M, MOGENSEN H S, ERIKSEN P S, et al. Yfiler® Plus population samples and dilution series: Stutters, analytic thresholds, and drop-out probabilities[J]. Int J Legal Med, 2017,131(6):1503-1511. doi:10.1007/s00414-017-1568-8 . |
| 18 | FOROUZESH M, IRANI S, SOLEIMANI A, et al. Application of Y-STR, DIP-STR and SNP-STR markers in interpretation of forensic genetic profiling: A narrative review[J]. Iran J Public Health, 2022,51(7):1538-1545. doi:10.18502/ijph.v51i7. 10087 . |
| 19 | CASTELLA V, GERVAIX J, HALL D. DIP-STR: Highly sensitive markers for the analysis of unbalanced genomic mixtures[J]. Human Mutation,2013,34(4):644-654. doi:10.1002/humu.22280 . |
| 20 | OLDONI F, CASTELLA V, GROSJEAN F, et al. Sensitive DIP-STR markers for the analysis of unbalanced mixtures from “touch” DNA samples[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2017,28:111-117. doi:10.10 16/j.fsigen.2017.02.004 . |
| 21 | TAN Y, WANG L, WANG H, et al. An investigation of a set of DIP-STR markers to detect unbalanced DNA mixtures among the southwest Chinese Han population[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2017,31:34-39. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2017.08.014 . |
| 22 | JIAN H, WANG L, LV M L, et al. A novel SNP-STR system based on a capillary electrophoresis platform[J]. Front Genet, 2021,12:636821. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.636821 . |
| 23 | LIU J D, LI W Y, WANG J Q, et al. A new set of DIP-SNP markers for detection of unbalanced and degraded DNA mixtures[J]. Electrophoresis, 2019,40(14):1795-1804. doi:10.1002/elps.201900017 . |
| 24 | LIU J D, HAO T, CHENG X J, et al. DIP-microhaplotypes: New markers for detection of unbalanced DNA mixtures[J]. Int J Leg Med,2021,135(1):13-21. doi:10.1007/s00414-020-02288-y . |
| 25 | WARD D, HENRY J, TAYLOR D. Analysis of mixed DNA profiles from the RapidHITTM ID platform using probabilistic genotyping software STRmixTM [J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2022,58:102664. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2022.102664 . |
| 26 | ALOTAIBI H, ALSOLAMI F, ABOZINADAH E, et al. TAWSEEM: A deep-learning-based tool for estimating the number of unknown contributors in DNA profiling[J]. Electronics, 2022,11(4):548. doi:10.3390/electronics11040548 . |
| 27 | BENSCHOP C C G, VAN DER LINDEN J, HOOGENBOOM J, et al. Automated estimation of the number of contributors in autosomal short tandem repeat profiles using a machine learning approach[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2019,43:102150. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2019.102150 . |
| 28 | MARCIANO M A, ADELMAN J D. PACE: Probabilistic Assessment for Contributor Estimation -- A machine learning-based assessment of the number of contributors in DNA mixtures[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2017,27:82-91. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2016.11.006 . |
| 29 | VALTL J, MÖNICH U J, LUN D S, et al. A series of developmental validation tests for number of contributors platforms: Exemplars using NOCIt and a neural network[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2021,54:102556. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2021.102556 . |
| 30 | 刘京,何光林,侯一平,等. 大规模平行测序在混合斑检测分析中的应用前景[J].法医学杂志, 2019,35(1):84-88,94. doi:10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2019.01.016 . |
| LIU J, HE G L, HOU Y P, et al. Application prospect of massively parallel sequencing in mixed stain detection[J]. Fayixue Zazhi, 2019,35(1):84-88,94. | |
| 31 | OLDONI F, KIDD K K, PODINI D. Microhaplotypes in forensic genetics[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2019,38:54-69. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2018. 09.009 . |
| 32 | PANG J B, RAO M, CHEN Q F, et al. A 124-plex microhaplotype panel based on next-generation sequencing developed for forensic applications[J]. Sci Rep, 2020,10:1945. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-58980-x . |
| 33 | CHEN A, XIONG L, QU Y, et al. Opportunity of next-generation sequencing-based short tandem repeat system for tumor source identification[J]. Front Oncol,2022,12:800028. doi:10.3389/fonc. 2022.800028 . |
| 34 | FAN H L, WANG L X, LIU C H, et al. Development and validation of a novel 133-plex forensic STR panel (52 STRs and 81 Y-STRs) using single-end 400 bp massive parallel sequencing[J]. Int J Legal Med,2022,136(2):447-464. doi:10.1007/s00414-021-027 38-1 . |
| 35 | CHENG K, SKILLMAN J, HICKEY S, et al. Variability and additivity of read counts for aSTRs in NGS DNA profiles[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2020,48:102351. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2020.102351 . |
| 36 | CHAN MUN WEI J, ZHAO Z C, LI S C, et al. NGS-based likelihood ratio for identifying contributors in two- and three-person DNA mixtures[J]. Comput Biol Chem,2018,74:428-433. doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.03.010 . |
| 37 | CORTES-FIGUEIREDO F, CARVALHO F S, FONSECA A C, et al. From forensics to clinical research: Expanding the variant calling pipeline for the precision ID mtDNA whole genome panel[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021,22(21):12031. doi:10.3390/ijms222112031 . |
| 38 | PALENCIA-MADRID L, VINUEZA-ESPINOSA D, BAETA M, et al. Validation of a 52-mtSNP minisequencing panel for haplogroup classification of forensic DNA samples[J]. Int J Legal Med,2020,134(3):929-936. doi:10.1007/s00414-020-02264-6 . |
| 39 | WISNER M, ERLICH H, SHIH S, et al. Resolution of mitochondrial DNA mixtures using a probe capture next generation sequencing system and phylogenetic-based software[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2021,53:102531. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2021. 102531 . |
| 40 | GROSJEAN F, FAVRE M, CASTELLA V. Comparison between MACSprepTM forensic sperm microbead kit and Erase Sperm Isolation kit for the enrichment of sperm fractions recovered from sexual assault samples[J]. Int J Legal Med,2023,137(1):267-278. doi:10.1007/s00414-022-02861-7 . |
| 41 | COSTA S, CORREIA-DE-SÁ P, PORTO M J, et al. The use of laser microdissection in forensic sexual assault casework: Pros and cons compared to standard methods[J]. J Forensic Sci,2017,62(4):998-1006. doi:10.1111/1556-4029.13348 . |
| 42 | VANDEWOESTYNE M, VAN NIEUWERBURGH F, VAN HOOFSTAT D, et al. Evaluation of three DNA extraction protocols for forensic STR typing after laser capture microdissection[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2012,6(2):258-262. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2011.06.002 . |
| 43 | JÄGER R. New perspectives for whole genome amplification in forensic STR analysis[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(13):7090. doi:10.3390/ijms23137090 . |
| 44 | HUFFMAN K, HANSON E, BALLANTYNE J. Probabilistic genotyping of single cell replicates from complex DNA mixtures recovers higher contributor LRs than standard analysis[J]. Sci Justice,2022,62(2):156-163. doi:10.1016/j.scijus.2022. 01.003 . |
| 45 | 马骏,童奇,高良弼,等. 尼龙膜套管分离技术对混合斑中精子细胞DNA的提取[J].法医学杂志,2018,34(4):417-419,427. doi:10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2018.04.015 . |
| MA J, TONG Q, GAO L B, et al. Extraction of DNA from sperm cells in mixed stain by nylon membrane bushing separation technique[J]. Fayixue Zazhi,2018,34(4):417-419,427. | |
| 46 | SAUER E, EXTRA A, CACHÉE P, et al. Identification of organ tissue types and skin from forensic samples by microRNA expression analysis[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2017,28:99-110. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2017.02.002 . |
| 47 | ZHANG X Y, LI J, LIU J D, et al. Identification of the vaginal secretion donor in mixture stains using polymorphic cSNPs on mRNA biomarkers[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2022,59:102703. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2022.102703 . |
| 48 | LIU J D, CHENG X J, LIU F, et al. Identification of coding region SNPs from specific and sensitive mRNA biomarkers for the deconvolution of the semen donor in a body fluid mixture[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2021,52:102483. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2021.102483 . |
| [1] | 姚彦汝, 金静, 王英杰, 张金专, 李英哲, 徐永新. 火场生物物证识别研究进展[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 64-69. |
| [2] | 胡文静, 杨婷婷, 王雅雅, 严江伟. 游离DNA最新研究进展及法医学应用展望[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 70-76. |
| [3] | 刘光渊. 应用多种遗传标记分析同母异父双胞胎亲子鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 106-108. |
| [4] | 董祎铭, 赵春梅, 陈念念, 罗丽, 李展鹏, 王利凯, 李晓倩, 任廷淦, 高彩荣, 郭相杰. 人工智能在法医学研究领域的文献可视化分析[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 1-14. |
| [5] | 云鹏, 陈安琪, 陈丽琴, 李成涛. 42个微单倍型复合检测体系的构建及法医学应用[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 50-58. |
| [6] | 黄逸航, 梁伟波, 蹇慧, 屈胜秋. 基于DNA甲基化推断年龄的建模方法与影响因素[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(6): 601-607. |
| [7] | 高林林, 谢炜, 朱素娟, 李达, 王琴, 洪亮, 李佑英. IDentifier DNA分型盒(炎黄34)的法医学验证及应用评估[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(6): 579-585. |
| [8] | 陶瑞旸, 王守宇, 袁春艳, 夏若成, 李成涛. 应用SNaPshot技术检测精液特异性cSNP遗传标记[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(5): 465-470. |
| [9] | 王中华, 李淑瑾. 人类身高推断的分子生物学研究进展[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(5): 487-492. |
| [10] | 张琦, 赵禾苗, 杨康, 陈静, 杨瑞琴, 王冲. 利用朴素贝叶斯和多元logistic回归构建月经血mRNA标志分析模型[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(5): 447-451. |
| [11] | 陈璐, 周喆, 王升启. 陈旧骸骨DNA身份鉴定的法医学进展[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(5): 478-486. |
| [12] | 郭科建, 黄磊, 李士林, 殷才湧, 汤真. 山东汉族人群37个Y-STR基因座多态性与突变调查[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(5): 501-506. |
| [13] | 杨乐, 丛欣, 陈冲, 贾莉, 李惠芬, 马云龙, 石妍. 应用多种遗传标记鉴定疑似父子关系的全同胞关系1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(4): 424-427. |
| [14] | 蒋志霞, 毛小慧, 衡素景. 母亲参与的姑侄亲缘关系鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(3): 326-328. |
| [15] | 白雪, 马冠车, 付丽红, 李淑瑾, 张晓静. 生父性侵女儿法医学鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2023, 39(3): 308-311. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||