

Journal of Forensic Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 267-276.DOI: 10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2024.340402
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qi LIAO1,2( ), Yong-hong LIU1, Ying JIAO1, Xiao-ying YANG1, Yi-hua YANG1, Cui-mei LIU3(
), Yong-hong LIU1, Ying JIAO1, Xiao-ying YANG1, Yi-hua YANG1, Cui-mei LIU3( ), Rui-xia GAO2(
), Rui-xia GAO2( )
)
Received:2024-04-01
Online:2025-08-29
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
Cui-mei LIU, Rui-xia GAO
CLC Number:
Qi LIAO, Yong-hong LIU, Ying JIAO, Xiao-ying YANG, Yi-hua YANG, Cui-mei LIU, Rui-xia GAO. Development of Benchtop Low‑Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Technology and Its Application in Drug Control Field[J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(3): 267-276.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.fyxzz.cn/EN/10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2024.340402
| 应用范围 | 样本来源 | 频率/MHz | 观测核 | 目的 | 检测物质 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合成大麻素类物质 | 海关缴获的“spice”样本 | 60 | 1H | 定性 | MAM-2201、JWH-073、JWH-210、JWH-122、JWH-081、JWH-250、UR-144、 XLR-11、 AKB-48-5F | [ |
| 合成大麻素类物质 | 海关扣押的电子烟油 | 60 | 1H, 19F | 定性、 定量 | JWH-210、5F-MDMB-PICA、5F-ADB、 5F-AKB48、ADB-FUBINACA | [ |
| 芬太尼类物质 | 购买的参考标准物质 | 62 | 1H | 定性 | 65种芬太尼类物质 | [ |
| 芬太尼类物质 | 自主合成 | 60 | 19F | 定性、 定量 | 8种含氟芬太尼类物质 | [ |
| 苯乙胺类物质 | 缴获的高纯度样品 | 60 | 1H | 定性 | 2C-B、2C-C、2C-D、 2C-E、 2C-P、 2C-T2、 2C-T7 | [ |
| 哌嗪类物质 | 购买的参考标准物质 | 60 | 1H | 定性 | 苄基哌嗪、2-PMP、3-PMP、 4-PMP | [ |
| 含氟新精神活性物质 | 购买的参考标准物质及缴获的含氟新精神活性物质样品 | 80 | 19F | 定性、 定量 | 51种合成大麻素类物质、8种合成卡西酮类物质、7种苯乙胺类物质、8种芬太尼类物质和9种其他类新精神活性物质 | [ |
| 传统阿片类、苯丙胺类、苯环利定类毒品 | 购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 80 | 1H | 定性 | 吗啡、海洛因、O3-单乙酰吗啡、O6-单乙酰吗啡、可待因、乙酰可待因、安非他明、甲基苯丙胺、MDA、MDMA、N,N-二甲基安非他明、氯胺酮 | [ |
| 非法减肥药 | 互联网平台购买含有不明成分的减肥药 | 60 | 1H | 定性 | 西布曲明和酚酞 | [ |
| MDMA | 缴获的实际样品 | 60 | 1H | 定量 | MDMA | [ |
| 植物大麻 | 购买的参考标准物质和市售的3种大麻制品 | 60 | 1H | 定量 | 四氢大麻酚、大麻二酚 | [ |
| 摇头丸及其混合物 | 缴获的实际样品 | 60 | 1H | 定量 | MDMA、咖啡因、苯佐卡因、非那西丁、利多卡因、左旋咪唑 | [ |
| 非法药物 | 购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 60 | 1H | 定性、 定量 | γ-羟基丁酸、可卡因、西布曲明、西地那非、他达拉非、咖啡因、对乙酰氨基酚、阿司匹林、双氯芬酸、布洛芬、萘普生 | [ |
| 甲基苯丙胺的前体和制毒配剂 | 制毒工厂采集的可疑固体和液体 | 43 | 1H, 31P | 定性 | 麻黄碱、伪麻黄碱、磷酸、亚磷酸、次磷酸 | [ |
| 冰毒及其混合物 | 购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 80 | 1H | 定性、 定量 | 甲基苯丙胺、咖啡因、二甲基砜、N-异丙基苄胺、非那西汀、吡拉西坦 | [ |
| 氯胺酮及其混合物 | 购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 80 | 1H | 定性、 定量 | 氯胺酮、磺胺、烟酰胺和非那西丁 | [ |
| 新精神活性物质自动化分析 | 购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 60 | 1H,19F, 1H-13C HSQC | 定性、 定量 | 包括卡西酮类、合成大麻素类、苯乙胺类、苯环利定类和芬太尼类等57种物质 | [ |
| 新精神活性物质自动化分析 | 自主合成、购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 60 | 1H | 定性 | 包括麻醉剂、新精神活性物质和管控物质,以及常见的非列管物质和掺假物等302种物质 | [ |
Tab. 1 Benchtop low‑field NMR spectroscopy for drugs and illicit substance analysis
| 应用范围 | 样本来源 | 频率/MHz | 观测核 | 目的 | 检测物质 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合成大麻素类物质 | 海关缴获的“spice”样本 | 60 | 1H | 定性 | MAM-2201、JWH-073、JWH-210、JWH-122、JWH-081、JWH-250、UR-144、 XLR-11、 AKB-48-5F | [ |
| 合成大麻素类物质 | 海关扣押的电子烟油 | 60 | 1H, 19F | 定性、 定量 | JWH-210、5F-MDMB-PICA、5F-ADB、 5F-AKB48、ADB-FUBINACA | [ |
| 芬太尼类物质 | 购买的参考标准物质 | 62 | 1H | 定性 | 65种芬太尼类物质 | [ |
| 芬太尼类物质 | 自主合成 | 60 | 19F | 定性、 定量 | 8种含氟芬太尼类物质 | [ |
| 苯乙胺类物质 | 缴获的高纯度样品 | 60 | 1H | 定性 | 2C-B、2C-C、2C-D、 2C-E、 2C-P、 2C-T2、 2C-T7 | [ |
| 哌嗪类物质 | 购买的参考标准物质 | 60 | 1H | 定性 | 苄基哌嗪、2-PMP、3-PMP、 4-PMP | [ |
| 含氟新精神活性物质 | 购买的参考标准物质及缴获的含氟新精神活性物质样品 | 80 | 19F | 定性、 定量 | 51种合成大麻素类物质、8种合成卡西酮类物质、7种苯乙胺类物质、8种芬太尼类物质和9种其他类新精神活性物质 | [ |
| 传统阿片类、苯丙胺类、苯环利定类毒品 | 购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 80 | 1H | 定性 | 吗啡、海洛因、O3-单乙酰吗啡、O6-单乙酰吗啡、可待因、乙酰可待因、安非他明、甲基苯丙胺、MDA、MDMA、N,N-二甲基安非他明、氯胺酮 | [ |
| 非法减肥药 | 互联网平台购买含有不明成分的减肥药 | 60 | 1H | 定性 | 西布曲明和酚酞 | [ |
| MDMA | 缴获的实际样品 | 60 | 1H | 定量 | MDMA | [ |
| 植物大麻 | 购买的参考标准物质和市售的3种大麻制品 | 60 | 1H | 定量 | 四氢大麻酚、大麻二酚 | [ |
| 摇头丸及其混合物 | 缴获的实际样品 | 60 | 1H | 定量 | MDMA、咖啡因、苯佐卡因、非那西丁、利多卡因、左旋咪唑 | [ |
| 非法药物 | 购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 60 | 1H | 定性、 定量 | γ-羟基丁酸、可卡因、西布曲明、西地那非、他达拉非、咖啡因、对乙酰氨基酚、阿司匹林、双氯芬酸、布洛芬、萘普生 | [ |
| 甲基苯丙胺的前体和制毒配剂 | 制毒工厂采集的可疑固体和液体 | 43 | 1H, 31P | 定性 | 麻黄碱、伪麻黄碱、磷酸、亚磷酸、次磷酸 | [ |
| 冰毒及其混合物 | 购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 80 | 1H | 定性、 定量 | 甲基苯丙胺、咖啡因、二甲基砜、N-异丙基苄胺、非那西汀、吡拉西坦 | [ |
| 氯胺酮及其混合物 | 购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 80 | 1H | 定性、 定量 | 氯胺酮、磺胺、烟酰胺和非那西丁 | [ |
| 新精神活性物质自动化分析 | 购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 60 | 1H,19F, 1H-13C HSQC | 定性、 定量 | 包括卡西酮类、合成大麻素类、苯乙胺类、苯环利定类和芬太尼类等57种物质 | [ |
| 新精神活性物质自动化分析 | 自主合成、购买的参考标准物质和缴获的实际样品 | 60 | 1H | 定性 | 包括麻醉剂、新精神活性物质和管控物质,以及常见的非列管物质和掺假物等302种物质 | [ |
| NPS种类 | 结构 | NPS数量 | 19F取代类型 | δF/×10-6(DMSO-d6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合成大麻素类 | 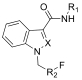 | 35 16 | (RCH2F) (para-ArF) | -217.0±0.2 -114.7±0.3 |
| 合成卡西酮类 | 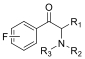 | 1 | (ortho-ArF) | -109.6 |
| 1 | (meta-ArF) | -111.5 | ||
| 6 | (para-ArF) | -103.1±0.4 | ||
| 苯乙胺类 | 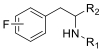 | 1 | (ortho-ArF) | -117.7 |
| 3 | (meta-ArF) | -113.3 | ||
| 3 | (para-ArF) | -116.2±0.1 | ||
| 哌嗪类 | 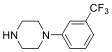 | 1 | TFMPP (ArCF3) 4-FPP (para-ArF) | -61.1 -123.6 |
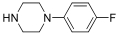 | 1 | |||
| 苯环利定类 | 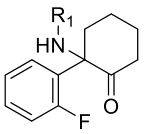 | 2 | 2-FDCK and 2-FXE (ortho-ArF) | -108.6±0.2 |
| 芬太尼类 | 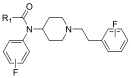 | 3 | (ortho-ArF) (meta-ArF) (para-ArF) | -119.5±0.2 -111.8 -113.7±0.3 |
| 1 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 苯二氮卓类 | 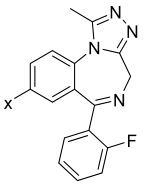 | 2 | Flubromazolam and Flualprazolam (ortho-ArF) | -114.0±0.1 |
| 其他 | 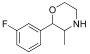 | 1 | 3-FPM (meta-ArF) 4-CF3-U47700 (ArCF3) | -112.7 -61.2 |
 | 1 |
Tab. 2 The 19F-NMR chemical shifts (0×10-6, referenced to CFCl3 ) of 83 fluorinated NPS
| NPS种类 | 结构 | NPS数量 | 19F取代类型 | δF/×10-6(DMSO-d6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合成大麻素类 |  | 35 16 | (RCH2F) (para-ArF) | -217.0±0.2 -114.7±0.3 |
| 合成卡西酮类 |  | 1 | (ortho-ArF) | -109.6 |
| 1 | (meta-ArF) | -111.5 | ||
| 6 | (para-ArF) | -103.1±0.4 | ||
| 苯乙胺类 |  | 1 | (ortho-ArF) | -117.7 |
| 3 | (meta-ArF) | -113.3 | ||
| 3 | (para-ArF) | -116.2±0.1 | ||
| 哌嗪类 |  | 1 | TFMPP (ArCF3) 4-FPP (para-ArF) | -61.1 -123.6 |
 | 1 | |||
| 苯环利定类 |  | 2 | 2-FDCK and 2-FXE (ortho-ArF) | -108.6±0.2 |
| 芬太尼类 |  | 3 | (ortho-ArF) (meta-ArF) (para-ArF) | -119.5±0.2 -111.8 -113.7±0.3 |
| 1 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 苯二氮卓类 |  | 2 | Flubromazolam and Flualprazolam (ortho-ArF) | -114.0±0.1 |
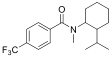
| 其他 |  | 1 | 3-FPM (meta-ArF) 4-CF3-U47700 (ArCF3) | -112.7 -61.2 |
 | 1 |
| [1] | 国家药监局 公安部 国家卫生健康委关于发布药用类麻醉药品和精神药品目录的公告(2025年第55号)[EB/OL].(2025-07-21)[2025-07-28]. |
| 19123.html | |
| Announcement by the National Medical Products Administration, Ministry of Public Security of the People’s Republic of China,National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China on adjusting the catalog of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances (No. 55 of 2025)[EB/OL]. (2025-07-21)[2025-07-28]. | |
| [2] | 吴波,郄一奇,杨乔,等. 盐酸氟胺酮的结构确证和核磁共振定量分析[J].刑事技术,2023,48(3):262-267. doi:10.16467/j.1008-3650.2022.0042 . |
| WU B, QIE Y Q, YANG Q, et al. Structural confirmation and quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance analysis into 2-fluoro-deschloroketamine hydrochloride[J]. Xingshi Jishu,2023,48(3):262-267. | |
| [3] | CASTAIN-CORDIER T, BOUILLAUD D, FARJON J, et al. Recent advances in benchtop NMR spectroscopy and its applications[M]// WEBB G A. Annual reports on NMR spectroscopy. Academic Press,2021,103:191-258. |
| [4] | 廖琦,贾薇,刘翠梅,等. 水峰压制-核磁共振波谱用于可疑饮料中γ-氨基丁酸、γ-羟基丁酸、γ-丁内酯和1,4-丁二醇的定性和定量分析[J].分析化学,2022,50(12):1907-1917. doi:10.19756/j.issn.0253-3820.210814 . |
| LIAO Q, JIA W, LIU C M, et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of γ-aminobutyric acid,γ-hydrox-ybutyric acid, γ-butyrolactone and 1,4-butanediol in suspicious beverages by water suppression-nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Fenxi Huaxue,2022,50(12):1907-1917. | |
| [5] | 唐泊伊,花镇东,王优美,等. 核磁共振扩散排序谱原位分离鉴定烟油中的美托尼秦[J].分析试验室,2025,44(7):963-969. doi:10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2024041102 . |
| TANG B Y, HUA Z D, WANG Y M, et al. In situ separation and identification of metonitazene in tobacco oil by nuclear magnetic resonance diffusion-ordered spectroscopy[J]. Fenxi Shiyanshi,2025,44(7):963-969. | |
| [6] | 栾佳琪,贾薇,花镇东,等. 核磁共振技术在新精神活性物质筛查中的应用[J].中国药科大学学报,2018,49(5):545-552. doi:10.11665/j.issn.1000-5048.20180505 . |
| LUAN J Q, JIA W, HUA Z D, et al. Applications of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the screening of new psychoactive substances[J]. Zhongguo Yaoke Daxue Xuebao,2018,49(5):545-552. | |
| [7] | GIBERSON J, SCICLUNA J, LEGGE N, et al. Developments in benchtop NMR spectroscopy 2015—2020[M]// WEBB G A. Annual reports on NMR spectroscopy. Academic Press,2021,102:153-246. |
| [8] | RIEGEL S D, LESKOWITZ G M. Benchtop NMR spectrometers in academic teaching[J]. TrAC Trends Anal Chem,2016,83:27-38. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2016.01.001 . |
| [9] | ASSEMAT G, BALAYSSAC S, GERDOVA A, et al. Benchtop low-field 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance for detecting falsified medicines[J]. Talanta,2019,196:163-173. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2018.12.005 . |
| [10] | GALVAN D, DE AGUIAR L M, BONA E, et al. Successful combination of benchtop nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and chemometric tools: A review[J]. Anal Chim Acta,2023,1273:341495. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2023.341495 . |
| [11] | DRAPER S L, MCCARNEY E R. Benchtop nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in forensic chemistry[J]. Magn Reson Chem,2023,61(2):106-129. doi:10.1002/mrc.5197 . |
| [12] | SANTOS A D C, DUTRA L M, MENEZES L R A, et al. Forensic NMR spectroscopy: Just a beginning of a promising partnership[J]. Trac Trends Anal Chem,2018,107:31-42. |
| [13] | ASSEMAT G, DUBOCQ F, BALAYSSAC S, et al. Screening of “spice” herbal mixtures: From high-field to low-field proton NMR[J]. Forensic Sci Int,2017,279:88-95. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2017.08.006 . |
| [14] | WU N, DANOUN S, BALAYSSAC S, et al. Synthetic cannabinoids in e-liquids: A proton and fluorine NMR analysis from a conventional spectrometer to a compact one[J]. Forensic Sci Int,2021,324:110813. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2021.110813 . |
| [15] | DUFFY J, URBAS A, NIEMITZ M, et al. Differentiation of fentanyl analogues by low-field NMR spectroscopy[J]. Anal Chim Acta,2019,1049:161-169. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2018.12.014 . |
| [16] | GILBERT N, MEWIS R E, SUTCLIFFE O B. Fast & fluorinated — Development and validation of a rapid benchtop NMR approach and other routine screening methods for the detection and quantification of synthesized fluorofentanyl derivatives[J]. Forensic Chem,2021,23:100321. doi:10.1016/j.forc. 2021.100321 . |
| [17] | ARANEDA J F, BAUMGARTE M, LANGE M, et al. Identification of seven psychedelic 2,5-dimethoxy-phenylethyl-amine-based designer drugs via benchtop 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. Magn Reson Chem,2023,61(2):66-72. doi:10.1002/mrc.5205 . |
| [18] | TENNANT T, HULME M C, ROBERTSON T B R, et al. Benchtop NMR analysis of piperazine-based drugs hyperpolarised by SABRE[J]. Magn Reson Chem,2020,58(12):1151-1159. doi:10.1002/mrc.4999 . |
| [19] | LIU C M, SONG C H, JIA W, et al. The application of 19F NMR spectroscopy for the analysis of fluorinated new psychoactive substances (NPS)[J]. Forensic Sci Int,2022,340:111450. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2022.111450 . |
| [20] | ZHONG Y, HUANG K, LUO Q, et al. The application of a desktop NMR spectrometer in drug analysis[J]. Int J Anal Chem,2018,2018:3104569. doi:10.1155/2018/3104569 . |
| [21] | WU N, BALAYSSAC S, DANOUN S, et al. Chemometric analysis of low-field 1H NMR spectra for unveiling adulteration of slimming dietary supplements by pharmaceutical compounds[J]. Molecules,2020,25(5):1193. doi:10.3390/molecules 25051193 . |
| [22] | HUSSAIN J H, GILBERT N, COSTELLO A, et al. Quantification of MDMA in seized tablets using benchtop 1H NMR spectroscopy in the absence of internal standards[J]. Forensic Chem,2020,20:100263. doi:10.1016/j.forc.2020.100263 . |
| [23] | ARANEDA J F, CHU T, LECLERC M C, et al. Quantitative analysis of cannabinoids using benchtop NMR instruments[J]. Anal Methods,2020,12(40):4853-4857. doi:10.1039/d0ay01511c . |
| [24] | FRINCULESCU A, MAIER A F G, SHINE T, et al. 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine quantification via benchtop 1H qNMR spectroscopy: Method validation and its application to ecstasy tablets collected at music festivals[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal,2022,214:114728. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114728 . |
| [25] | KEIZERS P H J, BAKKER F, FERREIRA J, et al. Benchtop NMR spectroscopy in the analysis of substandard and falsified medicines as well as illegal drugs[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal,2020,178:112939. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2019.112939 . |
| [26] | BOGUN B, MOORE S. 1H and 31P benchtop NMR of liquids and solids used in and/or produced during the manufacture of methamphetamine by the HI reduction of pseudoephedrine/ephedrine[J]. Forensic Sci Int,2017,278:68-77. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2017.06.026 . |
| [27] | 宋春辉,刘翠梅,贾薇,等. 低场和高场核磁共振技术用于甲基苯丙胺及其掺杂物定量分析[J].药物分析杂志,2023,43(5):793-803. doi:10.16155/j.0254-1793.2023.05.09 . |
| SONG C H, LIU C M, JIA W, et al. Quantitative analysis of methamphetamine and adulterants by low-field and high-field NMR[J]. Yaowu Fenxi Zazhi,2023,43(5):793-803. | |
| [28] | 刘翠梅,宋春辉,贾薇,等. 低场1H qNMR定量分析缴获毒品中氯胺酮及4种掺杂物[J].分析测试学报,2023,42(6):755-761. doi:10.19969/j.fxcsxb.23013002 . |
| LIU C M, SONG C H, JIA W, et al. Quantification of ketamine and four kinds of adulterants in seized drugs by low-field 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. Fenxi Ceshi Xuebao,2023,42(6):755-761. | |
| [29] | CASTAING-CORDIER T, BENAVIDES RESTREPO A, DUBOIS D, et al. Characterization of new psychoactive substances by integrating benchtop NMR to multi-technique databases[J]. Drug Test Anal,2022,14(9):1629-1638. doi:10.1002/dta.3332 . |
| [30] | ANTONIDES L H, BRIGNALL R M, COSTELLO A, et al. Rapid identification of novel psychoactive and other controlled substances using low-field 1H NMR spectroscopy[J]. ACS Omega,2019,4(4):7103-7112. doi:10.1021/acsomega.9b00302 . |
| [31] | PURCELL E M, TORREY H C, POUND R V. Resonance absorption by nuclear magnetic moments in a solid[J]. Phys Rev,1946,69(1/2):37-38. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.69.37 . |
| [32] | HAHN E L, MAXWELL D E. Chemical shift and field independent frequency modulation of the spin echo envelope[J]. Phys Rev,1951,84(6):1246-1247. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.84.1246 . |
| [33] | YU F C, PROCTOR W G. The dependence of a nuclear magnetic resonance frequency upon chemical compound[J]. Phys Rev,1950,77(5):717. |
| [34] | BECKER E D, FISK C L, KHETRAPAL C L. Development of NMR From the Early Beginnings to the Early 1990s[M]// Encyclopedia of Magnetic Resonance. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2007:18-28. doi:10.1002/9780470034590.emrhp0001 . |
| [35] | 刘莲花,蒋滨,陈代谢,等. 超导磁共振仪器设备国产化现状及挑战[J].波谱学杂志,2022,39(3):345-355. doi:10.11938/cjmr20212961 . |
| LIU L H, JIANG B, CHEN D X, et al. The status and challenge of the domestic manufacturing of superconduct magnetic resonance instruments in China[J]. Bopuxue Zazhi,2022,39(3):345-355. | |
| [36] | BLÜMICH B. Low-field and benchtop NMR[J]. J Magn Reson,2019,306:27-35. doi:10.1016/j.jmr. 2019.07.030 . |
| [37] | ZAPATA F, MATEY J M, MONTALVO G, et al. Chemical classification of new psychoactive substances (NPS)[J]. Microchem J,2021,163:105877. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2020.105877 . |
| [38] | 施妍,周莉英,沈保华,等. 毛发中7种常见合成大麻素类新精神活性物质的分析及应用[J].法医学杂志,2021,37(4):479-485,492. doi:10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2021.310301 . |
| SHI Y, ZHOU L Y, SHEN B H, et al. Analysis and application of seven common new psychoactive substances of synthetic cannabinoids in hair[J]. Fayixue Zazhi,2021,37(4):479-485,492. | |
| [39] | 范一雷,陈显鑫,薛锦锋,等. 新型靛红腙类合成大麻素质谱裂解规律研究[J].分析试验室,2024,43(1):57-63. doi:10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2023.032002 . |
| FAN Y L, CHEN X X, XUE J F, et al. Investigation of mass spectrometry-based fragmentation patterns of new “OXIZID” synthetic cannabinoids[J]. Fenxi Shiyanshi,2024,43(1):57-63. | |
| [40] | 朱娜,俞晨,花镇东,等. 哌嗪类新精神活性物质的质谱特征研究[J].质谱学报,2021,42(1):1-7. doi:10.7538/zpxb.2019.0161 . |
| ZHU N, YU C, HUA Z D, et al. Mass fragmentation characteristics of piperazine analogues[J]. Zhipu Xuebao,2021,42(1):1-7. | |
| [41] | 周晓力,李增鑫,刘万卉,等. 核磁共振技术的定量方法综述[J].药物分析杂志,2024,44(10):1655-1664. doi:10.16155/j.0254-1793.2023-0803 . |
| ZHOU X L, LI Z X, LIU W H, et al. A review of nuclear magnetic resonance quantitative technique[J]. Yaowu Fenxi Zazhi,2024,44(10):1655-1664. | |
| [42] | HOLZGRABE U, DEUBNER R, SCHOLLMAYER C, et al. Quantitative NMR spectroscopy — Applications in drug analysis[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal,2005,38(5):806-812. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2005.01.050 . |
| [43] | 常祥文,陈文茜,孙艳,等. 大麻的潜在医疗价值及使用风险[J].中国药物依赖性杂志,2020,29(3):161-168. doi:10.13936/j.cnki.cjdd1992.2020.03.001 . |
| CHANG X W, CHEN W X, SUN Y, et al. Potential medical use and risks of cannabis[J]. Zhongguo Yaowu Yilaixing Zazhi,2020,29(3):161-168. | |
| [44] | JAYASHREE B S, NIKHIL P S, PAUL S. Bioisosterism in drug discovery and development — An overview[J]. Med Chem,2022,18(9):915-925. doi:10.2174/1573406418666220127124228 . |
| [45] | WILLIAM R, DOLBIER. Guide to fluorine NMR for Organic Chemists[M]. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley,2009:9-21. |
| [46] | 钱振华,李静,花镇东. 麻黄碱、伪麻黄碱及(1S,2S)-β-氯代甲基苯丙胺、(1R,2S)-β-氯代甲基苯丙胺的分析方法研究[J].中国司法鉴定,2017(5):36-41. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2072.2017.05.006 . |
| QIAN Z H, LI J, HUA Z D. Analysis of ephedrine, pseudophedrine, (1S,2S)-β-chloro-methamphetamine and(1R,2S)-β-chloro-methamphetamine[J]. Zhongguo Sifa Jianding,2017(5):36-41. | |
| [47] | 郑晓雨,赵彦彪,闻武,等. 基于非目标筛查技术的甲基苯丙胺合成路线分析[J].刑事技术,2023,48(6):577-583. doi:10.16467/j.1008-3650.2023.0020 . |
| ZHENG X Y, ZHAO Y B, WEN W, et al. Non-targeted profiling of methamphetamine in China[J]. Xingshi Jishu,2023,48(6):577-583. | |
| [48] | 刘培培,吴健美,樊颖锋,等. 氯胺酮杂质的超高效液相色谱-质谱法分析及其关联性判别应用[J].分析科学学报,2019,35(2):182-186. doi:10.13526/j.issn.1006-6144.2019.02.009 . |
| LIU P P, WU J M, FAN Y F, et al. Impurity profiling of ketamine and its applications on correlation analysis[J]. Fenxi Kexue Xuebao,2019,35(2):182-186. | |
| [49] | BELMONTE-SÁNCHEZ J R, ROMERO-GONZÁLEZ R, OROSA M Á M, et al. Benchtop NMR spectroscopy for quantitative determination of milk fat and qualitative determination of lactose: From calibration curve to deep learning[J]. LWT,2024,212:117000. |
| [1] | Yi-fan BAI, He-miao ZHAO, Jing CHEN, Hong-di LIU, Rui-qin YANG, Chong WANG. Application of Forensic Transcriptomics in the Identification of Tissue Origin of Body Fluid Stains [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(3): 260-266. |
| [2] | Xuan-long CHEN, Qiang YUAN, Yong SUN, Die ZHANG, Jian-bin FU, Li-liang LI. Forensic Research Progress on Bongkrekic Acid Poisoning [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(2): 111-119. |
| [3] | Shuai ZHANG, Hong-fei XU, Zhi-xiang ZHANG, Ying WANG, Shao-hua ZHU. Research on Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity Mechanism and Its Forensic Application [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(2): 120-126. |
| [4] | Yu-meng ZUO, Wei HAN, Jian-bo ZHANG, Tao LI. Molecular Mechanisms and Toxic Effects of Ketamine [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(2): 127-135. |
| [5] | Zhuo LI, Yi-ru ZENG, Zhi-long SHU, Xue-hong SUN, Kui ZHANG. Research Status of Caenorhabditis elegans Model in Toxicology and Its Applications in Forensic Science [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(2): 136-143. |
| [6] | Cheng-tao LI, Bin CONG. Thoughts on the Development of Forensic Medicine Discipline Standing at a New Historical Starting Point [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(1): 9-14. |
| [7] | Hong-yu SUN, Hu ZHAO. Seventy Years of Passing on the Torch, Striving Forward in the New Era — Thoughts on the Construction of Forensic Medicine at Sun Yat-sen University [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(1): 20-24. |
| [8] | Shu-jin LI, Chun-ling MA, Bin CONG. Uphold Fundamental Principles and Break New Ground and Work Persistently to Build a First-Class Forensic Medicine Discipline [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(1): 5-8. |
| [9] | Guang CHEN, Rong-shuai WANG, Li SU, Yue ZHANG, Xue-xia LIU, Shi-yong FANG, Zhan-zhan LIU, Ya-jun XU, Xiang XU. Thoughts and Practices on the Development of Forensic Medicine Discipline in the Perspective of Building a Regional High-Level Medical University [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(1): 35-39. |
| [10] | Dong-fang QIAO, Ping-ming QIU, Qi WANG, Yun-chun TAI, Dong-ri LI, Jing-tao XU, Qi-zhi LUO, En-ping HUANG, Bo-feng ZHU. Guided by National Strategic Needs, Striving to Build a First-Class Forensic Medicine Discipline — The Construction Plan for Forensic Medicine at Southern Medical University [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(1): 15-19. |
| [11] | Zhi-wen WEI, Hong-xing WANG, Jun-hong SUN, Hao-liang FAN, Hong-liang SU, Le-le WANG, Wen-ting HE, Zhe CHEN, Jie ZHANG, Xiang-jie GUO, Ji LI, Geng-qian ZHANG, Xin-hua LIANG, Jiang-wei YAN, Qiang-qiang ZHANG, Cai-rong GAO, Ying-yuan WANG, Hong-wei WANG, Jun XIE, Bo-feng ZHU, Ke-ming YUN. Creation and Exploration of the “Organized Fill-in-the-Blank Format” Discipline Construction Model for Forensic Medicine in the New Era [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(1): 25-29. |
| [12] | Wei-bo LIANG. Construction and High-Quality Development of Forensic Medicine Discipline at Sichuan University [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(1): 30-34. |
| [13] | Zun-lei QIAN, Meng-qi WU, Yu SHI. Effects of Common Anticoagulants on the Visual Characteristics of Bloodstains [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(1): 40-47,58. |
| [14] | Kai HE, Jin-long YUAN, Chang-mao QIU, Ze-jun LIU, Yuan-feng QI, Zhen-hui GAO. Analysis of the Development and Implementation of the Environmental Damage Compensation System in Japan [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(1): 74-82. |
| [15] | Jiao-jiao JI, Xin WANG, Jia-man LIN, Duo-qi XU, Hui YAN, Min SHEN. Research Progress on the Application of MALDI-MSI in Hair Analysis [J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2024, 40(6): 542-549. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||