

法医学杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 217-227.DOI: 10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2024.541105
谢宝颜1,2( ), 夏若成2(
), 夏若成2( ), 蒋婷婷3, 陶瑞旸2(
), 蒋婷婷3, 陶瑞旸2( ), 李成涛1,4(
), 李成涛1,4( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-28
发布日期:2025-09-15
出版日期:2025-06-25
通讯作者:
陶瑞旸,李成涛
作者简介:谢宝颜(1998—),男,硕士研究生,主要从事法医遗传学研究;E-mail:2022110052@stu.immu.edu.cn基金资助:
Bao-yan XIE1,2( ), Ruo-cheng XIA2(
), Ruo-cheng XIA2( ), Ting-ting JIANG3, Rui-yang TAO2(
), Ting-ting JIANG3, Rui-yang TAO2( ), Cheng-tao LI1,4(
), Cheng-tao LI1,4( )
)
Received:2024-11-28
Online:2025-09-15
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
Rui-yang TAO, Cheng-tao LI
摘要:
目的 分析Web of Science核心合集(Web of Science Core Collection,WoSCC)数据库中2000—2023年收录的法医学体液鉴定研究领域文献,探索该领域的研究现状、热点及发展趋势。 方法 利用CiteSpace软件对2000—2023年WoSCC数据库中收录的法医学体液鉴定领域文献进行可视化分析。同时,对文献的年发文量、期刊分布、国家贡献、研究机构、作者合作、关键词进行文献计量分析。 结果 共纳入715篇法医学体液鉴定领域的文献,年发文量呈持续且稳定增长的趋势。在55个发文国家(地区)中,美国以174篇文献位居首位,中国次之,共发表了107篇。在发表期刊方面,载文量最多的期刊是Forensic Science International: Genetics,在该杂志上发表的文献占总发文量的20%。在作者贡献方面,共2 079位作者参与了体液鉴定的相关研究,作者合作网络图谱呈现出明显的聚类分布。关键词分析结果表明,法医学体液鉴定领域的研究热点主要聚焦于传统方法、特异性RNA分子标记、DNA甲基化、光谱法以及微生物组学的应用。 结论 法医学体液鉴定领域的研究成果丰富,研究机构和团队应加强合作。建立统一的结果解读标准与体系、探索多种生物标记的联用方法是该领域未来研究的热点与重要方向。
中图分类号:
谢宝颜, 夏若成, 蒋婷婷, 陶瑞旸, 李成涛. 法医学体液鉴定研究的文献计量及可视化分析[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 217-227.
Bao-yan XIE, Ruo-cheng XIA, Ting-ting JIANG, Rui-yang TAO, Cheng-tao LI. Bibliometric and Visual Analysis of Forensic Research on Body Fluid Identification[J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(3): 217-227.
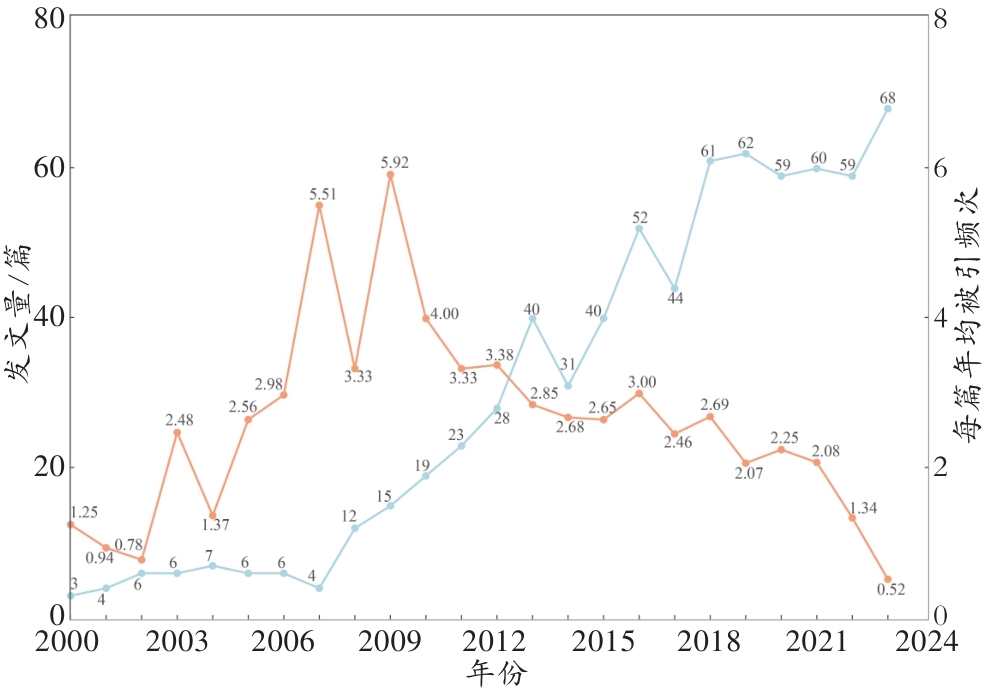
图1 2000—2023年法医学体液鉴定领域发文量及年均被引趋势蓝色曲线表示发文量;红色曲线表示被引频次。
Fig. 1 Publication volume and trends in average annual citations in the field of forensic body fluididentification from 2000 to 2023
| 期刊 | 发文量/篇 | h指数 | g指数 | m指数 | 被引频次 | 影响因子 | 分区 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forensic Science International: Genetics | 143 | 39 | 56 | 2.167 | 3 997 | 3.2 | Q1 |
| Forensic Science International | 80 | 27 | 52 | 1.080 | 2 785 | 2.2 | Q1 |
| Journal of Forensic Sciences | 76 | 23 | 40 | 0.920 | 1 727 | 1.5 | Q2 |
| International Journal of Legal Medicine | 62 | 22 | 41 | 1.000 | 1 802 | 2.2 | Q1 |
| Science & Justice | 43 | 16 | 23 | 0.696 | 586 | 1.9 | Q2 |
| Analytical Chemistry | 29 | 11 | 11 | 0.688 | 550 | 6.7 | Q1 |
| Electrophoresis | 22 | 11 | 18 | 1.000 | 335 | 3.0 | Q2 |
| Legal Medicine | 12 | 10 | 16 | 0.714 | 311 | 1.3 | Q3 |
| Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry | 11 | 9 | 9 | 0.600 | 343 | 3.8 | Q1 |
| Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine | 9 | 8 | 11 | 0.667 | 134 | 1.2 | Q3 |
表1 发文量排名前十期刊的发文量及评价指标
Tab. 1 Publication volume and evaluation indexes of the top 10 journals ranked by publication volume
| 期刊 | 发文量/篇 | h指数 | g指数 | m指数 | 被引频次 | 影响因子 | 分区 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forensic Science International: Genetics | 143 | 39 | 56 | 2.167 | 3 997 | 3.2 | Q1 |
| Forensic Science International | 80 | 27 | 52 | 1.080 | 2 785 | 2.2 | Q1 |
| Journal of Forensic Sciences | 76 | 23 | 40 | 0.920 | 1 727 | 1.5 | Q2 |
| International Journal of Legal Medicine | 62 | 22 | 41 | 1.000 | 1 802 | 2.2 | Q1 |
| Science & Justice | 43 | 16 | 23 | 0.696 | 586 | 1.9 | Q2 |
| Analytical Chemistry | 29 | 11 | 11 | 0.688 | 550 | 6.7 | Q1 |
| Electrophoresis | 22 | 11 | 18 | 1.000 | 335 | 3.0 | Q2 |
| Legal Medicine | 12 | 10 | 16 | 0.714 | 311 | 1.3 | Q3 |
| Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry | 11 | 9 | 9 | 0.600 | 343 | 3.8 | Q1 |
| Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine | 9 | 8 | 11 | 0.667 | 134 | 1.2 | Q3 |
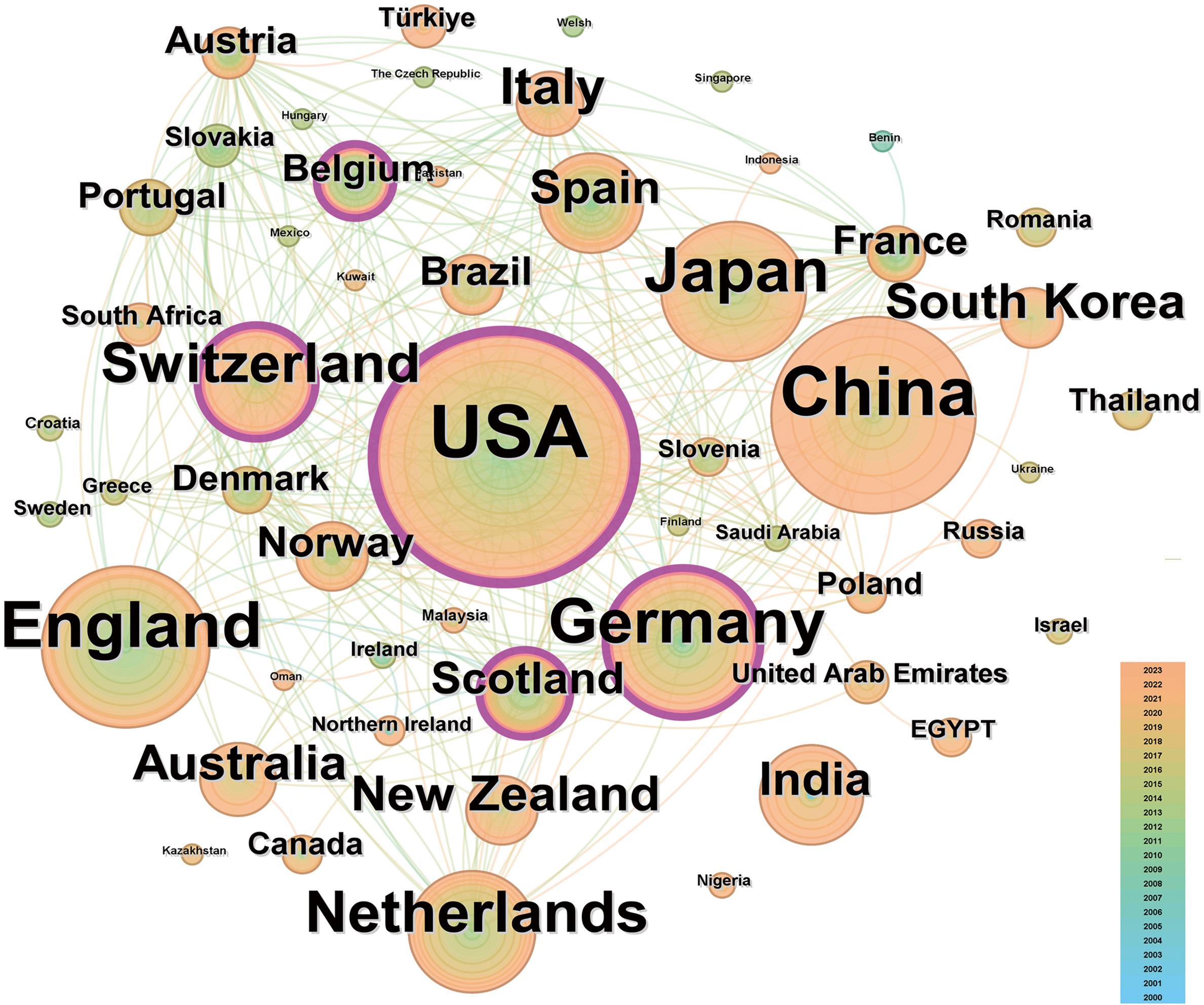
图2 法医学体液鉴定领域国家(地区)合作共现网络图谱节点大小代表国家(地区)的发文量,节点越大即发文量越高;外圈标记为粉紫色的节点表示其中介中心性>0.1,节点内圈的颜色代表发文年份;节点之间连线的粗细代表合作关系的强弱,颜色对应节点代表首次共现的时间。
Fig. 2 Co-occurrence network map for countries (regions)cooperation in the field of forensicbody fluid identification
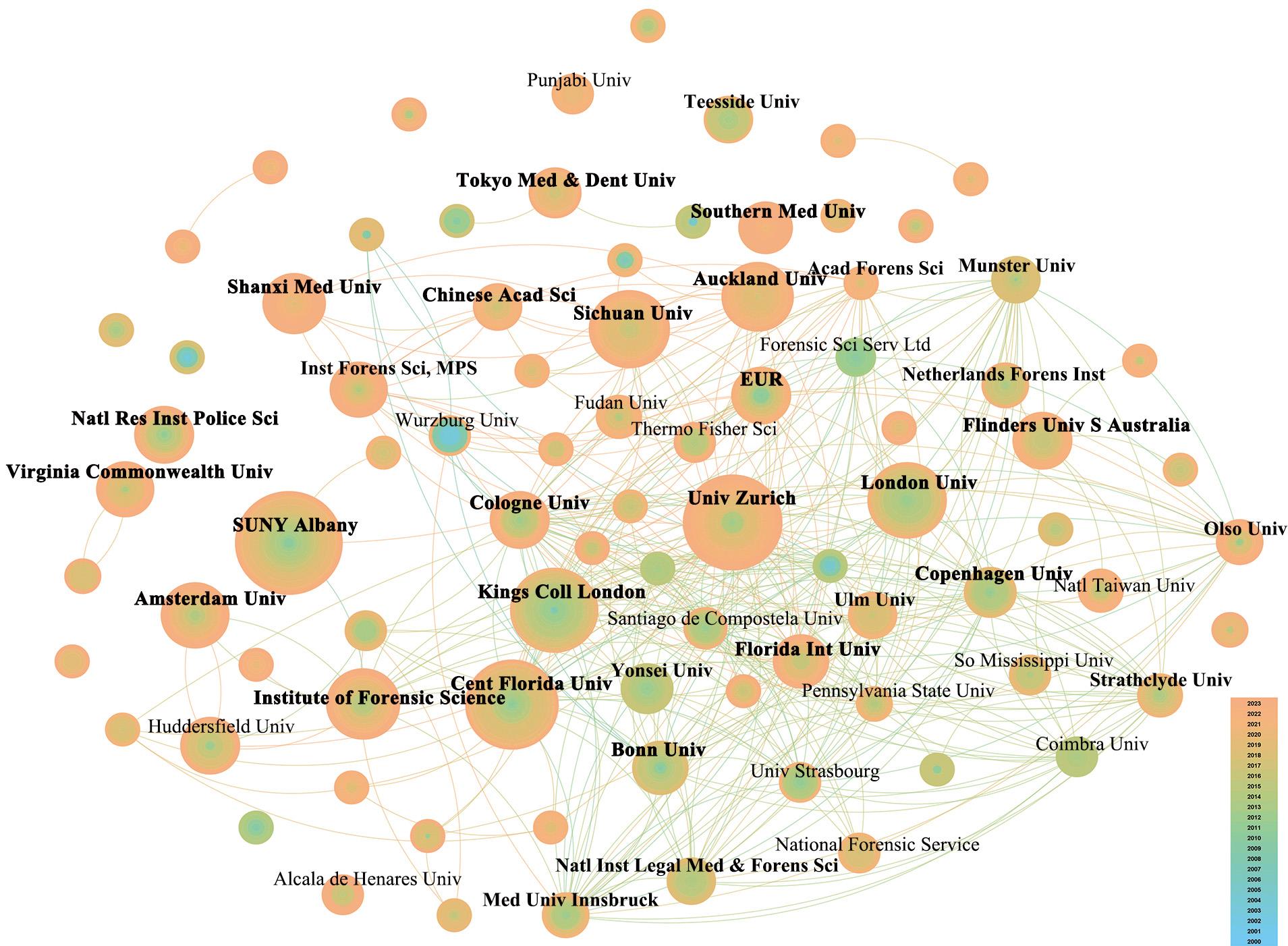
图3 法医学体液鉴定领域机构合作共现网络图谱节点大小代表机构的发文量,节点越大即发文量越高;节点内圆圈的颜色代表发文年份;节点之间连线的粗细代表合作关系的强弱,颜色对应节点代表首次共现的时间。
Fig. 3 Co-occurrence network map for institutionalcooperation in the field of forensicbody fluid identification
| 作者 | 发文量/篇 | 被引频次 | h指数 | g指数 | m指数 | 起始发文年份 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lednev,IK | 46 | 2 516 | 26 | 46 | 1.529 | 2008 |
| Haas,C | 30 | 1 174 | 19 | 30 | 1.188 | 2009 |
| Ballantyne,J | 29 | 1 756 | 21 | 29 | 1.000 | 2004 |
| Sijen,T | 17 | 921 | 15 | 17 | 1.071 | 2011 |
| Akutsu,T | 27 | 412 | 14 | 19 | 0.933 | 2010 |
| Watanabe,K | 26 | 412 | 14 | 19 | 0.933 | 2010 |
| Kayser,M | 15 | 1 266 | 14 | 15 | 0.824 | 2008 |
| Hanson,E | 18 | 683 | 13 | 18 | 0.929 | 2011 |
| Sakurada,K | 23 | 324 | 13 | 17 | 0.867 | 2010 |
| Berti,A | 13 | 498 | 11 | 13 | 0.579 | 2006 |
表2 发文量排名前十作者的被引频次及其科学评价指数
Tab. 2 Citation frequencies and scientific evaluation indexes of the top 10 authors ranked by publication volume
| 作者 | 发文量/篇 | 被引频次 | h指数 | g指数 | m指数 | 起始发文年份 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lednev,IK | 46 | 2 516 | 26 | 46 | 1.529 | 2008 |
| Haas,C | 30 | 1 174 | 19 | 30 | 1.188 | 2009 |
| Ballantyne,J | 29 | 1 756 | 21 | 29 | 1.000 | 2004 |
| Sijen,T | 17 | 921 | 15 | 17 | 1.071 | 2011 |
| Akutsu,T | 27 | 412 | 14 | 19 | 0.933 | 2010 |
| Watanabe,K | 26 | 412 | 14 | 19 | 0.933 | 2010 |
| Kayser,M | 15 | 1 266 | 14 | 15 | 0.824 | 2008 |
| Hanson,E | 18 | 683 | 13 | 18 | 0.929 | 2011 |
| Sakurada,K | 23 | 324 | 13 | 17 | 0.867 | 2010 |
| Berti,A | 13 | 498 | 11 | 13 | 0.579 | 2006 |
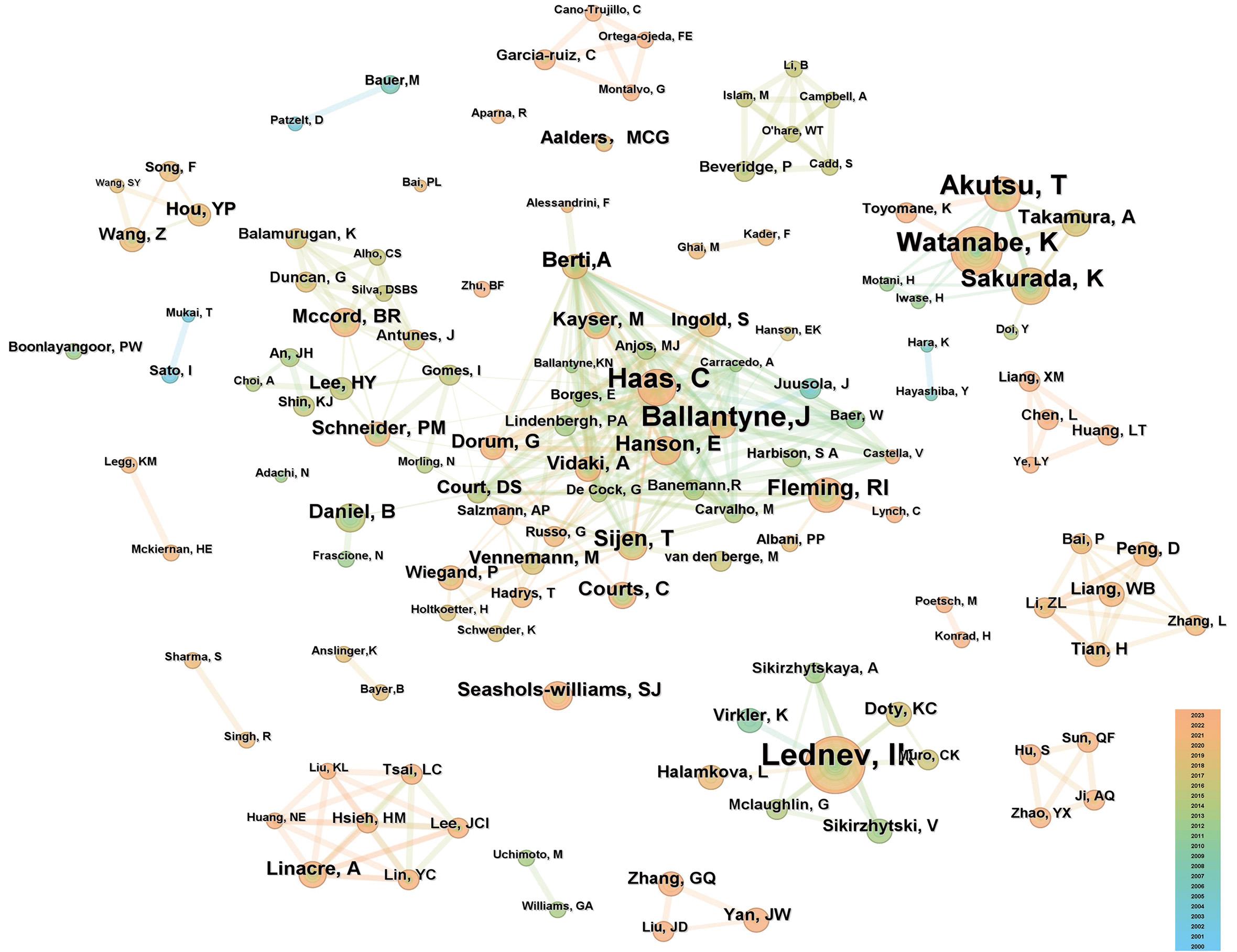
图4 法医学体液鉴定领域作者合作共现网络图谱节点大小代表作者的发文量,节点越大即发文量越多;节点内圈的颜色代表发文年份;节点之间连线的粗细代表合作关系的强弱,颜色对应节点代表首次共现的时间。
Fig. 4 Co-occurrence network map for author cooperation in the field of forensic body fluid identification
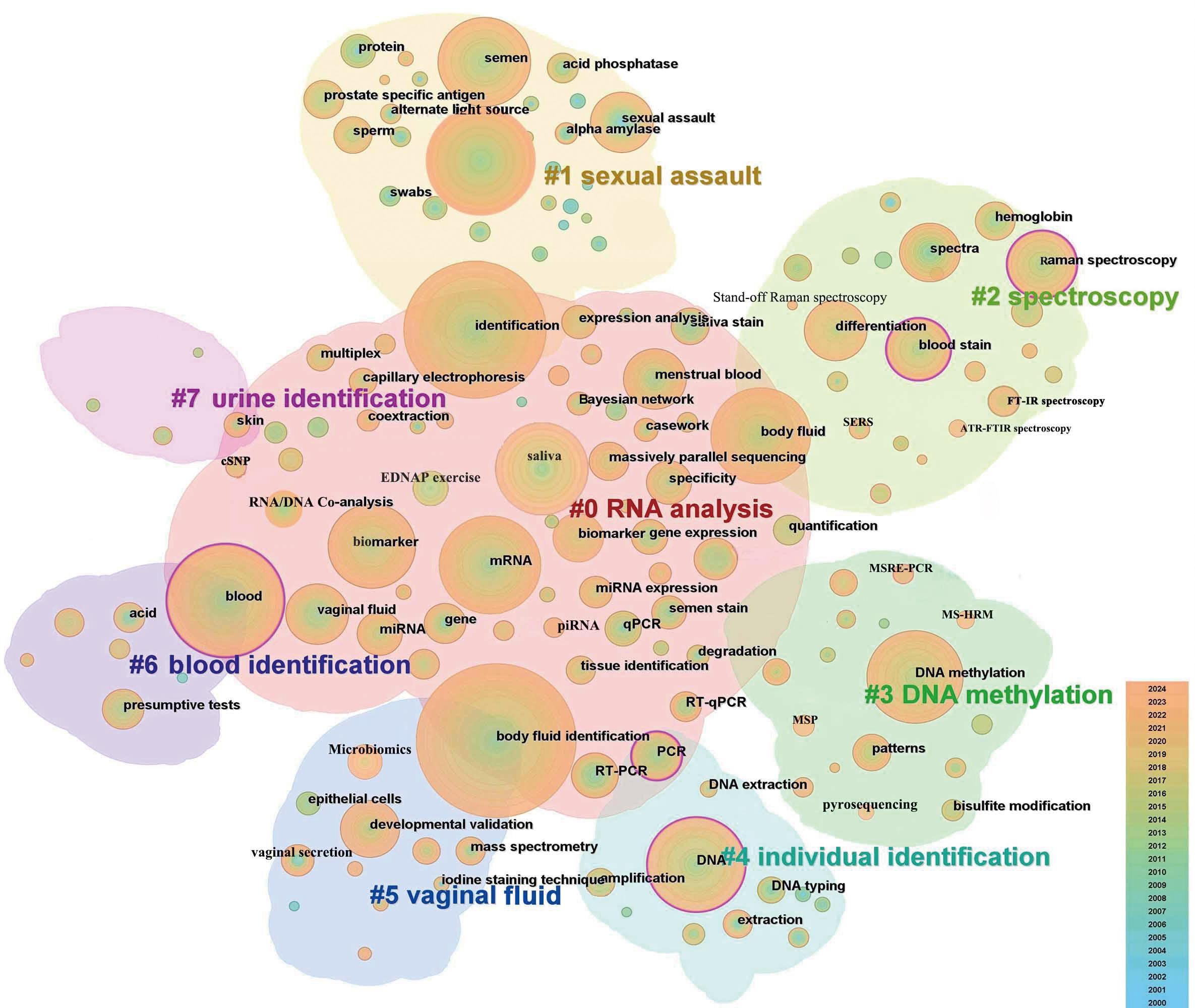
图5 法医学体液鉴定领域关键词聚类共现网络图谱节点大小代表关键词出现的频次,节点越大即频次越高;节点外圈的粉色表示该节点中介中心性>0.1,节点内圈的颜色代表发文年份,颜色对应节点代表首次共现的时间。
Fig. 5 Co-occurrence network map for keywords clustering in the field of forensic body fluid identification
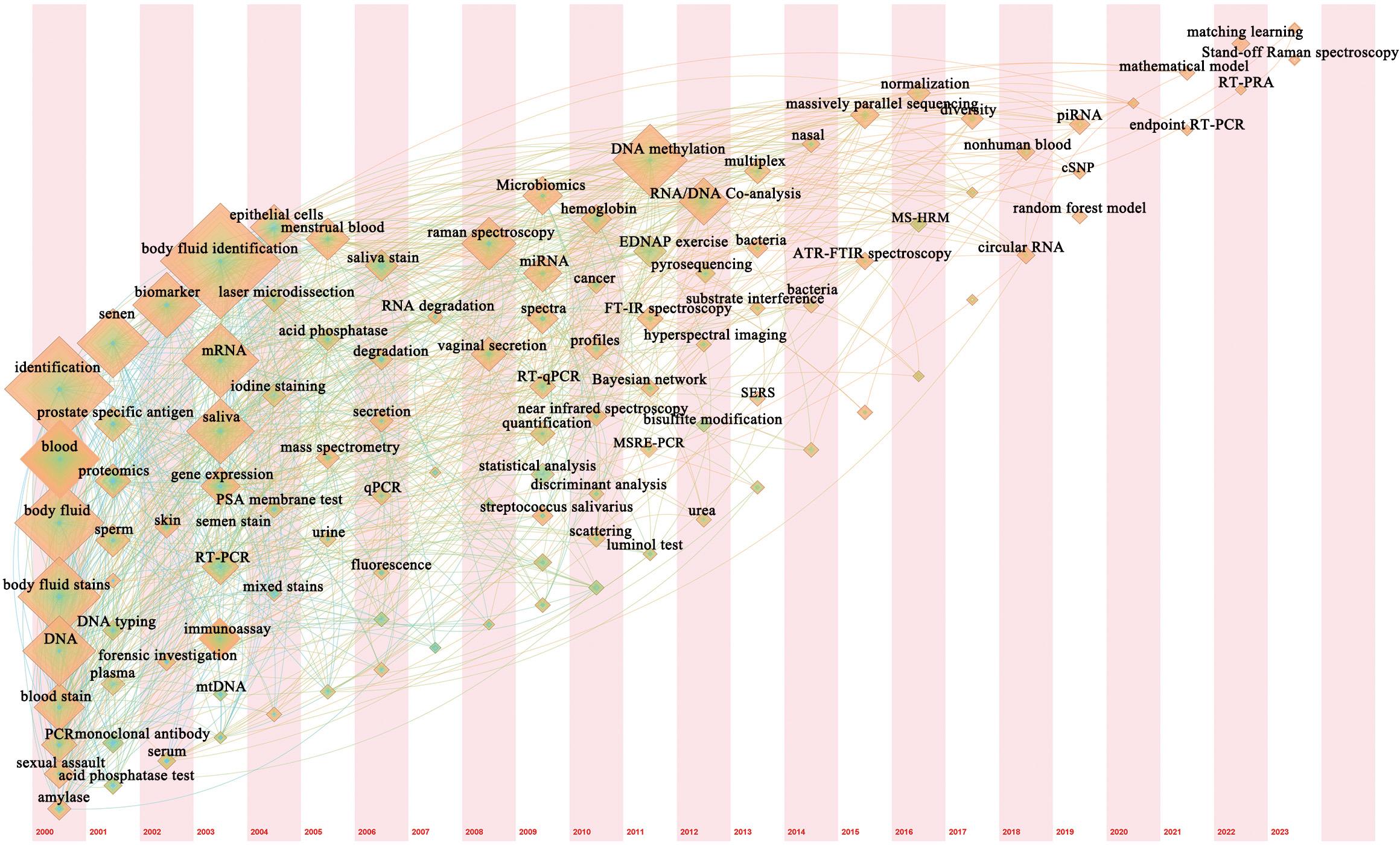
图6 法医学体液鉴定领域关键词时区图谱节点大小代表关键词出现的频次,节点越大即频次越高;节点所在位置代表其首次出现的年份,节点内圈的颜色代表发文年份;节点之间连线的粗细代表关键词间联系的强弱,颜色对应节点代表首次共现的时间。
Fig. 6 Timezone map for keywords in the field of forensic body fluid identification
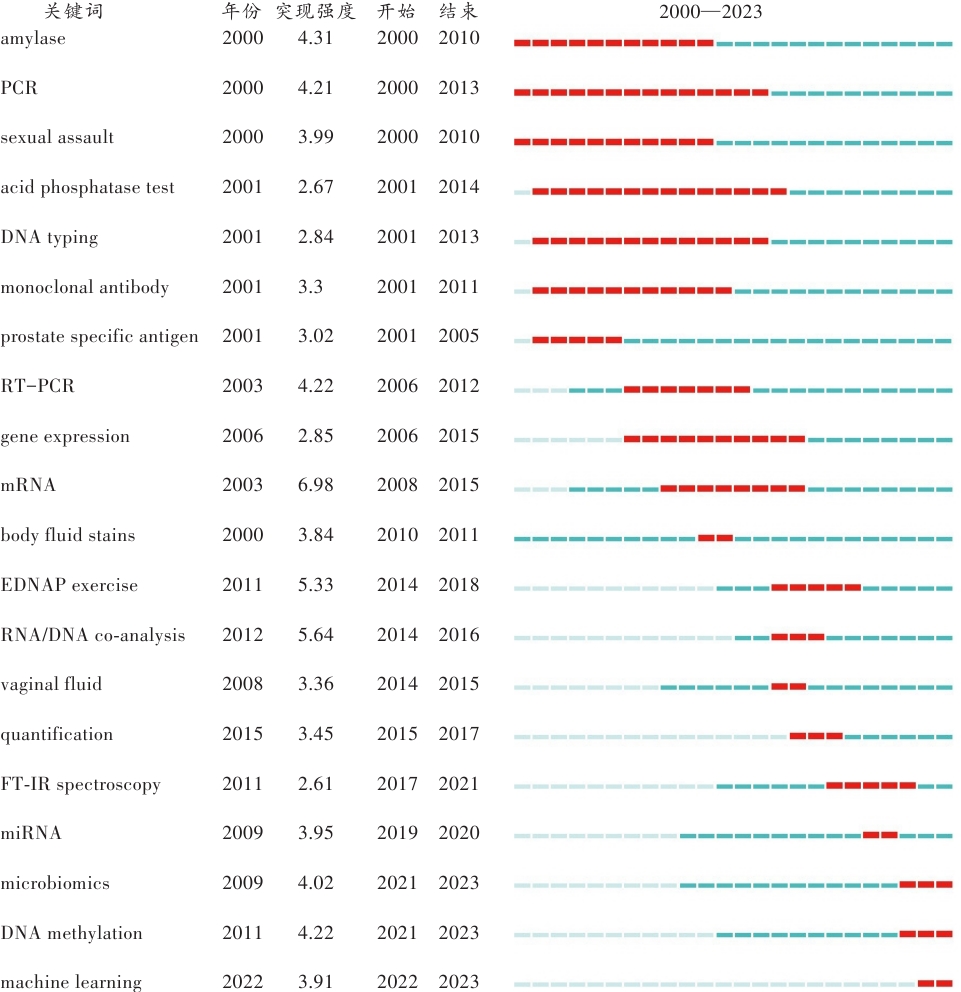
图7 2000—2023年法医学体液鉴定领域的突现关键词每个单元格代表1年的时间跨度,深蓝色表示在该年度内此关键词出现,而红色则表示发文数量激增持续的时期。
Fig. 7 Burst keywords in the field of forensic bodyfluid identification from 2000 to 2023
| [1] | LIU Y, HE H, XIAO Z X, et al. A systematic analysis of miRNA markers and classification algorithms for forensic body fluid identification[J]. Brief Bioinform,2021,22(4):bbaa324. doi:10.1093/bib/bbaa324 . |
| [2] | KAYSER M, DE KNIJFF P. Improving human forensics through advances in genetics, genomics and molecular biology[J]. Nat Rev Genet,2011,12(3):179-192. doi:10.1038/nrg2952 . |
| [3] | HIRSCH J E. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2005,102(46):16569-16572. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507655102 . |
| [4] | BORNMANN L, MUTZ R, DANIEL H D. Are there better indices for evaluation purposes than the h index? A comparison of nine different variants of the h index using data from biomedicine[J]. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol,2008,59(5):830-837. doi:10.1002/asi.20806 . |
| [5] | EGGHE L. Theory and practise of the g-index[J]. Scientometrics,2006,69(1):131-152. doi:10.1007/s11192-006-0144-7 . |
| [6] | SONG M, ZHANG J, LIU X H, et al. Developments and trends in energy poverty research — Li-terature visualization analysis based on CiteSpace[J]. Sustainability,2023,15(3):2576. doi:10.3390/su150 32576 . |
| [7] | VIRKLER K, LEDNEV I K. Raman spectroscopy offers great potential for the nondestructive confirmatory identification of body fluids[J]. Forensic Sci Int,2008,181(1/2/3):e1-e5. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint. 2008.08.004 . |
| [8] | KISTENEV Y V, BORISOV A V, SAMARINOVA A A, et al. A novel Raman spectroscopic method for detecting traces of blood on an interfering substrate[J]. Sci Rep,2023,13(1):5384. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31918-9 . |
| [9] | SIKIRZHYTSKAYA A, SIKIRZHYTSKI V, PÉREZ-ALMODÓVAR L, et al. Raman spectroscopy for the identification of body fluid traces: Semen and vaginal fluid mixture[J]. Forensic Chem,2023,32:100468. doi:10.1016/j.forc.2023.100468 . |
| [10] | HAAS C, HANSON E, ANJOS M J, et al. RNA/DNA co-analysis from human menstrual blood and vaginal secretion stains: Results of a fourth and fifth collaborative EDNAP exercise[J]. Forensic Science International: Genetics,2014,8(1):203-212. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2013.09.009 . |
| [11] | HAAS C, HANSON E, KRATZER A, et al. Selection of highly specific and sensitive mRNA biomarkers for the identification of blood[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2011,5(5):449-458. doi:10.1016/j.fsi gen.2010.09.006 . |
| [12] | HANSON E, INGOLD S, HAAS C, et al. Messenger RNA biomarker signatures for forensic body fluid identification revealed by targeted RNA sequencing[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2018,34:206-221. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.02.020 . |
| [13] | JOHANNESSEN H, HANSON E, GILL P, et al. Body fluid identification in samples collected after intimate and social contact: A comparison of two mRNA profiling methods and the additional information gained by cSNP genotypes[J]. Genes (Basel),2023,14(3):636. doi:10.3390/genes14030636 . |
| [14] | AN J H, SHIN K J, YANG W I, et al. Body fluid identification in forensics[J]. BMB Rep,2012,45(10):545-553. doi:10.5483/bmbrep.2012.45.10.206 . |
| [15] | QUICKENDEN T I, CREAMER J I. A study of common interferences with the forensic luminol test for blood[J]. Luminescence,2001,16(4):295-298. doi:10.1002/bio.657 . |
| [16] | SATO I, YOSHIIKE M, YAMASAKI T, et al. A dot-blot-immunoassay for semen identification using a polyclonal antibody against semenogelin, a powerful seminal marker[J]. Forensic Sci Int,2001,122(1):27-34. doi:10.1016/S0379-0738(01)00435-2 . |
| [17] | FEINE I, GAFNY R, PINKAS I. Combination of prostate-specific antigen detection and micro-Raman spectroscopy for confirmatory semen detection[J]. Forensic Sci Int,2017,270:241-247. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.10.012 . |
| [18] | HOLTKÖTTER H, SCHWENDER K, WIEGAND P, et al. Improving body fluid identification in forensic trace evidence — Construction of an immunochromatographic test array to rapidly detect up to five body fluids simultaneously[J]. Int J Legal Med,2018,132(1):83-90. doi:10.1007/s00414-017-1724-1 . |
| [19] | HAAS C, KLESSER B, MAAKE C, et al. mRNA profiling for body fluid identification by reverse transcription endpoint PCR and realtime PCR[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2009,3(2):80-88. doi:10. 1016/j.fsigen.2008.11.003 . |
| [20] | HANSON E K, LUBENOW H, BALLANTYNE J. Identification of forensically relevant body fluids using a panel of differentially expressed microRNAs[J]. Anal Biochem,2009,387(2):303-314. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2009.01.037 . |
| [21] | WANG Z, ZHANG J, WEI W, et al. Identification of saliva using microRNA biomarkers for forensic purpose[J]. J Forensic Sci,2015,60(3):702-706. doi:10.1111/1556-4029.12730 . |
| [22] | ZUBAKOV D, BOERSMA A W M, CHOI Y, et al. microRNA markers for forensic body fluid identification obtained from microarray screening and quantitative RT-PCR confirmation[J]. Int J Legal Med,2010,124(3):217-226. doi:10.1007/s00414-009-0402-3 . |
| [23] | COURTS C, MADEA B. Specific micro-RNA signatures for the detection of saliva and blood in forensic body-fluid identification[J]. J Forensic Sci,2011,56(6):1464-1470. doi:10.1111/j.1556-4029. 2011.01894.x . |
| [24] | HANSON E, INGOLD S, HAAS C, et al. Targeted multiplexed next generation RNA sequencing assay for tissue source determination of forensic samples[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet Suppl Ser,2015,5:e441-e443. doi:10.1016/j.fsigss.2015.09.175 . |
| [25] | LIU J, CHENG X, LIU F, et al. Identification of coding region SNPs from specific and sensitive mRNA biomarkers for the deconvolution of the semen donor in a body fluid mixture[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2021,52:102483. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen. 2021.102483 . |
| [26] | ZHANG X, LI J, LIU J, et al. Identification of the vaginal secretion donor in mixture stains using polymorphic cSNPs on mRNA biomarkers[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2022,59:102703. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2022.102703 . |
| [27] | HANSON E, DØRUM G, ZAMBORLIN M, et al. Targeted S5 RNA sequencing assay for the identification and direct association of common body fluids with DNA donors in mixtures[J]. Int J Legal Med,2023,137(1):13-32. doi:10.1007/s00414-022-02908-9 . |
| [28] | LIU B, YANG Q, MENG H, et al. Development of a multiplex system for the identification of forensically relevant body fluids[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2020,47:102312. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2020. 102312 . |
| [29] | WANG S, WANG Z, TAO R, et al. Expression profile analysis of piwi-interacting RNA in forensically relevant biological fluids[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2019,42:171-180. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2019. 07.015 . |
| [30] | BACQUET J, MAGDINIER F, LEONETTI G, et al. Estimation of medico-legal age through the study of DNA methylation: Review of the literature[J]. La Revue de Médecine Légale,2019,10(4):129-139. doi:10.1016/j.medleg.2019.07.001 . |
| [31] | FRUMKIN D, WASSERSTROM A, BUDOWLE B, et al. DNA methylation-based forensic tissue identification[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2011,5(5):517-524. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2010.12.001 . |
| [32] | LI Z, LI Y, LIU N, et al. Typing of semen-containing mixtures using ARMS-based semen-specific CpG-InDel/STR markers[J]. Int J Legal Med,2022,136(4):1163-1176. doi:10.1007/s00414-022-02843-9 . |
| [33] | WATANABE K, TANIGUCHI K, AKUTSU T. Development of a DNA methylation-based semen-specific SNP typing method: A new approach for genotyping from a mixture of body fluids[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2018,37:227-234. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.09.004 . |
| [34] | WATANABE K, TANIGUCHI K, TOYOMANE K, et al. A new approach for forensic analysis of saliva-containing body fluid mixtures based on SNPs and methylation patterns of nearby CpGs[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2022,56:102624. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2021.102624 . |
| [35] | DOTY K C, MURO C K, BUENO J, et al. What can Raman spectroscopy do for criminalistics?[J]. J Raman Spectrosc,2016,47(1):39-50. doi:10.1002/jrs.4826 . |
| [36] | GEORGE N, SINGH H, JOTANIYA R, et al. Raman spectroscopy for the determination of forensically important bio-fluids[J]. Forensic Sci Int,2022,340:111441. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2022.111441 . |
| [37] | BOYD S, BERTINO M F, YE D, et al. Highly sensitive detection of blood by surface enhanced Raman scattering[J]. J Forensic Sci,2013,58(3):753-756. doi:10.1111/1556-4029.12120 . |
| [38] | ALMEHMADI L M, LEDNEV I K. Stand-off Raman spectroscopy is a promising approach for the detection and identification of bloodstains for forensic purposes[J]. J Raman Spectrosc,2024,55(2):227-231. doi:10.1002/jrs.6609 . |
| [39] | SIKIRZHYTSKI V, SIKIRZHYTSKAYA A, LEDNEV I K. Multidimensional Raman spectroscopic signatures as a tool for forensic identification of body fluid traces: A review[J]. Appl Spectrosc,2011,65(11):1223-1232. doi:10.1366/11-06455 . |
| [40] | ELKINS K M. Rapid presumptive “fingerprinting” of body fluids and materials by ATR FT-IR spectroscopy[J]. J Forensic Sci,2011,56(6):1580-1587. doi:10.1111/j.1556-4029.2011.01870.x . |
| [41] | TAKAMURA A, WATANABE K, AKUTSU T, et al. Soft and robust identification of body fluid using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and chemometric strategies for forensic analysis[J]. Sci Rep,2018,8(1):8459. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-26873-9 . |
| [42] | NICHOLS N A, LEDNEV I K. Raman spectroscopy for forensic identification of body fluid traces: Method validation for potential false negatives caused by blood-affecting diseases[J]. Am J Analyt Chem,2022,13(1):1-8. doi:10.4236/ajac.2022.131001 . |
| [43] | MURO C K, DOTY K C, DE SOUZA FERNANDES L, et al. Forensic body fluid identification and differentiation by Raman spectroscopy[J]. Forensic Chem,2016,1:31-38. doi:10.1016/j.forc. 2016.06.003 . |
| [44] | ACHETIB N, FALKENA K, SWAYAMBHU M, et al. Specific fluorescent signatures for body fluid identification using fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Sci Rep,2023,13(1):3195. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-30241-7 . |
| [45] | KUMARI P, PRAKASH P, YADAV S, et al. Microbiome analysis: An emerging forensic investigative tool[J]. Forensic Sci Int,2022,340:111462. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2022.111462 . |
| [46] | WOHLFAHRT D, TAN-TORRES A L, GREEN R, et al. A bacterial signature-based method for the identification of seven forensically relevant human body fluids[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet,2023,65:102865. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2023.102865 . |
| [47] | AKUTSU T, MOTANI H, WATANABE K, et al. Detection of bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA genes for forensic identification of vaginal fluid[J]. Leg Med (Tokyo),2012,14(3):160-162. doi:10.1016/j.legalmed.2012.01.005 . |
| [48] | GIAMPAOLI S, DEVITTORI E, VALERIANI F, et al. Informativeness of NGS analysis for vaginal fluid identification[J]. J Forensic Sci,2017,62(1):192-196. doi:10.1111/1556-4029.13222 . |
| [49] | CHEN X, XU H, ZHU B. Forensic validation of a combined analysis of mRNA and miRNA markers for precise tissue origin inferences of five kinds of body fluids by RT-qPCR[J]. Electrophoresis,2023, 44(21/22):1714-1724. doi:10.1002/elps.202300059 . |
| [50] | LIU B, SONG F, YANG Q, et al. Characterization of tissue-specific biomarkers with the expression of circRNAs in forensically relevant body fluids[J]. Int J Legal Med,2019,133(5):1321-1331. doi:10.1007/s00414-019-02027-y . |
| [51] | CHOI A, SHIN K J, YANG W I, et al. Body fluid identification by integrated analysis of DNA methylation and body fluid-specific microbial DNA[J]. Int J Legal Med,2014,128(1):33-41. doi:10.1007/s00414-013-0918-4 . |
| [1] | 陈静, 王亚萍, 冯云鹏, 胡晓欣, 贾振军, 刘洪迪, 严安心, 李永久, 彭柱, 刘志芳, 陈健刚. 国产人类DNA定量试剂盒的验证及法医学应用[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 252-259. |
| [2] | 李泽琴, 原芳, 刘娜, 严江伟, 张更谦. 牙线来源的生物样本采集、DNA提取及STR分型[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 237-243. |
| [3] | 刘志勇, 任贺, 陈冲, 高知枭, 石妍, 李林, 贾莉, 杨倩, 刘雅诚, 严江伟. D13S317基因座侧翼序列突变及稀有等位基因4确认1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 294-296. |
| [4] | 白一帆, 赵禾苗, 陈静, 刘洪迪, 杨瑞琴, 王冲. 法医转录组学技术在体液斑迹组织来源推断中的应用[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 260-266. |
| [5] | 何曦, 汤真, 夏明英, 赵一琦, 罗雨然, 李士林. 基于CODIS核心13个常染色体STR基因座分析不同群体中的遗传结构[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 228-236. |
| [6] | 孙晓琦, 黄娅琳. 投毒案件中曼陀罗物种鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(1): 104-106. |
| [7] | 沈高芳, 周咏松, 张健球, 嵇世有, 吴应锋, 尚昊, 朱波峰. DNA实验室人源性DNA污染TaqMan qPCR检测方法的建立及应用[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(1): 66-73. |
| [8] | 章俊, 潘立鹏, 陈安琪, 陈吉. 三个体组合同胞关系鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(6): 624-627. |
| [9] | 刘振平, 阿地来·吐尔逊, 傅燕芳, 童继军, 吴玉茹, 翟仙敦. 男性样本Amelogenin-Y、DYS391、rs199815934同时缺失1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(6): 628-632. |
| [10] | 刘京, 王正, 侯一平, 廖林川. STR突变对亲缘关系鉴定的影响[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(5): 484-491. |
| [11] | 韩俊萍, 王颖希, 刘超, 刘锋, 郭晋荣, 朱巍, 唐光峰, 李彩霞, 王鑫, 焦章平. 国产Quick TargSeq全集成自动化现场快速DNA检测仪的测试评估[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(5): 461-467. |
| [12] | 蔡美铭, 台运春, 陈玲, 邱平明, 袁曦, 吴晓连, 孙煜钦, 朱波峰. “CBL+PBL”模式在法医物证教学中的应用[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(4): 387-390. |
| [13] | 吴黎明, 陈安琪, 张素华, 李成涛. 基于不同STR分型试剂盒的肿瘤组织身源鉴定方法[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(4): 330-339. |
| [14] | 靳铭辉, 李亚, 易少华. 人体表微生物组应用于法医学个体识别的研究进展[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(4): 379-386. |
| [15] | 孟必成, 何柏芳, 姚智卿, 王斌, 黄江平, 郝思静, 曹禹, 余华光, 杨帆. 利用法医SNP系谱推断技术侦破命案积案1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2024, 40(4): 406-407. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||