

法医学杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 340-347.DOI: 10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2025.350403
• 论著快检技术赋能法医毒物学多场景应用专题 • 上一篇 下一篇
何泰伸( ), 吕中将, 孙一铭, 李雨洋, 叶懿, 林瑶(
), 吕中将, 孙一铭, 李雨洋, 叶懿, 林瑶( ), 廖林川(
), 廖林川( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-15
发布日期:2025-11-25
出版日期:2025-08-25
通讯作者:
林瑶,廖林川
作者简介:何泰伸(2004—),男,主要从事法医毒物分析研究;E-mail:373049588@qq.com
基金资助:
Tai-shen HE( ), Zhong-jiang LÜ, Yi-ming SUN, Yu-yang LI, Yi YE, Yao LIN(
), Zhong-jiang LÜ, Yi-ming SUN, Yu-yang LI, Yi YE, Yao LIN( ), Lin-chuan LIAO(
), Lin-chuan LIAO( )
)
Received:2025-04-15
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-08-25
Contact:
Yao LIN, Lin-chuan LIAO
摘要:
目的 建立一种基于比率荧光探针的氰化物快速分析方法,为氰化物的现场可视化快速检测提供定量策略。 方法 以牛血清白蛋白稳定的金纳米团簇(gold nanoclusters,AuNCs;荧光发射波长为660 nm)作为响应单元,荧光素(fluorescein,FL;发射波长为515 nm)作为内参,构建金纳米团簇与荧光素(AuNCs-FL)双发射比率荧光探针。 结果 氰化物对AuNCs的刻蚀作用导致660 nm处荧光淬灭,而FL在515 nm处荧光信号保持不变,通过红色到绿色的荧光变化实现氰化物的快速分析。该荧光探针可在3 min内完成检测,检出限为3.4 mg/L,可视化检测范围为10~100 mg/L。 结论 AuNCs-FL荧光探针组成简单、成本较低,操作简单且快速准确,可避免氰化物检测试剂盒易受硫化物干扰的问题,能够满足氰化物中毒案件中可疑粉末检材的现场快速检测。
中图分类号:
何泰伸, 吕中将, 孙一铭, 李雨洋, 叶懿, 林瑶, 廖林川. 基于金纳米团簇-荧光素比率荧光探针的氰化物快速分析[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 340-347.
Tai-shen HE, Zhong-jiang LÜ, Yi-ming SUN, Yu-yang LI, Yi YE, Yao LIN, Lin-chuan LIAO. Rapid Analysis of Cyanide Based on a Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe Using Gold Nanoclusters-Fluorescein[J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2025, 41(4): 340-347.
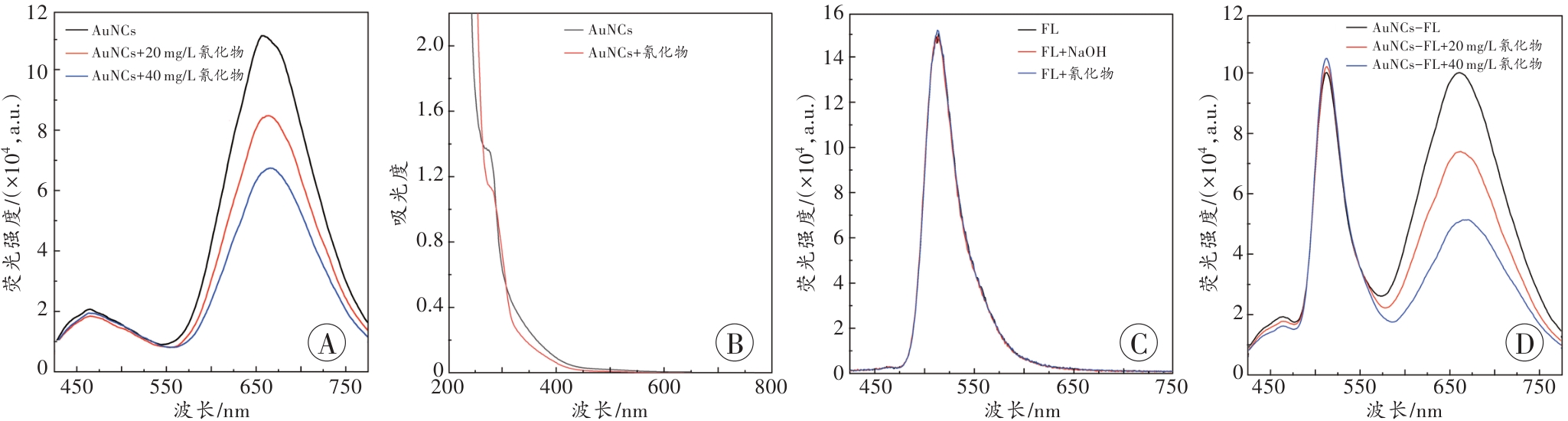
图3 所构建比率荧光探针的光谱表征图像A:AuNCs和氰化物反应前后的荧光光谱图;B:AuNCs和氰化物反应前后的紫外-可见吸收光谱图;C:FL与NaOH和氰化物共存时的荧光光谱图;D:AuNCs-FL探针与氰化物反应的荧光光谱图。
Fig. 3 Spectral characterization images of the constructed ratiometric fluorescent probe
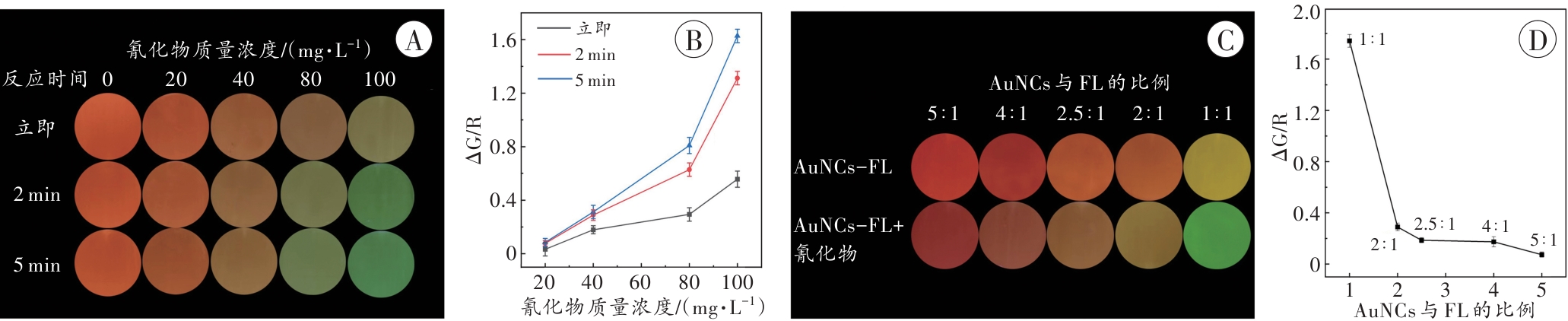
图4 AuNCs-FL探针与氰化物反应条件的优化A:探针与氰化物反应不同时间的荧光图像;B:探针与氰化物反应不同时间的ΔG/R值折线图;C:AuNCs与FL不同体积比获得的荧光图像;D:AuNCs与FL在不同体积比时的ΔG/R值折线图。
Fig. 4 Optimization of reaction conditions for the AuNCs-FL probe and cyanide
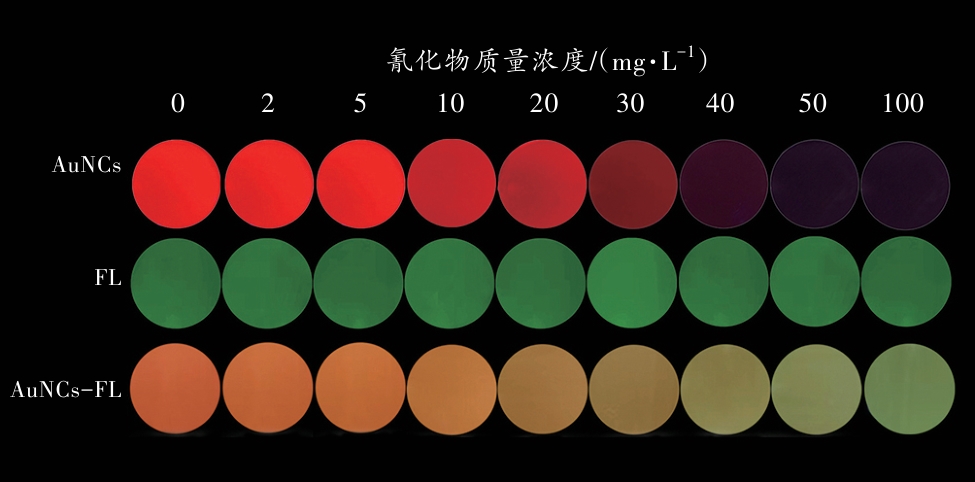
图5 单一AuNCs、FL以及AuNCs-FL与系列质量浓度氰化物反应后的荧光图像
Fig. 5 Fluorescence images of single AuNCs, FL,as well as AuNCs-FL after reacting with cyanideat a series of mass concentrations
| 氰化物荧光分析方法 | 检出限 | 反应时间 | 便携式检测装置 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碳点-AuNCs法 | 0.15 μmol/L | - | 无 | [ |
| 香豆素探针法 | 0.22 μmol/L | - | 无 | [ |
| 氰乙烯基探针法 | 12.4 nmol/L | 30 s | 无 | [ |
| 三重荧光探针法 | 45 nmol/L | >13 min | 无 | [ |
| Benzo-Hemicyanine法 | 0.43 μmol/L | - | 无 | [ |
| 罗丹明B衍生物法 | 0.33 μmol/L | 30 min | 无 | [ |
| Hg-石墨烯量子点法 | 3.1 μmol/L | 5 min | 无 | [ |
| Calixarene法 | 0.115 μmol/L | - | 无 | [ |
| HBT-Br-thiazolium法 | 1.79 μmol/L | 2 min | 试纸 | [ |
| 三苯胺有机探针法 | 36 nmol/L | 4 min | 试纸 | [ |
| 聚集诱导发光活性分子法 | 6.17 nmol/L | - | 试纸 | [ |
| AuNCs-FL法 | 52.3 μmol/L | 2 min | 便携式装置(可读数) | 本研究 |
表1 本方法与其他氰化物荧光分析方法的性能对比
Tab. 1 Performance comparison between this method and other fluorescent analysis methods for cyanide
| 氰化物荧光分析方法 | 检出限 | 反应时间 | 便携式检测装置 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碳点-AuNCs法 | 0.15 μmol/L | - | 无 | [ |
| 香豆素探针法 | 0.22 μmol/L | - | 无 | [ |
| 氰乙烯基探针法 | 12.4 nmol/L | 30 s | 无 | [ |
| 三重荧光探针法 | 45 nmol/L | >13 min | 无 | [ |
| Benzo-Hemicyanine法 | 0.43 μmol/L | - | 无 | [ |
| 罗丹明B衍生物法 | 0.33 μmol/L | 30 min | 无 | [ |
| Hg-石墨烯量子点法 | 3.1 μmol/L | 5 min | 无 | [ |
| Calixarene法 | 0.115 μmol/L | - | 无 | [ |
| HBT-Br-thiazolium法 | 1.79 μmol/L | 2 min | 试纸 | [ |
| 三苯胺有机探针法 | 36 nmol/L | 4 min | 试纸 | [ |
| 聚集诱导发光活性分子法 | 6.17 nmol/L | - | 试纸 | [ |
| AuNCs-FL法 | 52.3 μmol/L | 2 min | 便携式装置(可读数) | 本研究 |
| 样品 | 氰化物加标质量浓度/(mg·L-1) | 检测值/( | 回收率/% | RSD/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白糖 | 30 | 30.7±0.6 | 102.3 | 1.2 |
| 淀粉 | 30 | 26.0±1.8 | 86.7 | 4.5 |
| 泥土 | 30 | 29.9±2.2 | 99.7 | 4.4 |
表2 3种样品氰化物加标后的检测值和回收率
Tab. 2 Detection values and recovery rates of three types of samples spiked with cyanide
| 样品 | 氰化物加标质量浓度/(mg·L-1) | 检测值/( | 回收率/% | RSD/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白糖 | 30 | 30.7±0.6 | 102.3 | 1.2 |
| 淀粉 | 30 | 26.0±1.8 | 86.7 | 4.5 |
| 泥土 | 30 | 29.9±2.2 | 99.7 | 4.4 |
| [1] | 廖林川. 法医毒物分析[M].5版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2016:119-121. |
| LIAO L C. Forensic toxicological analysis[M]. 5th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House,2016:119-121. | |
| [2] | 陈东. 医源性氰化物积蓄中毒案例鉴定探讨[J].中国法医学杂志,2024,39(S1):75-76. doi:10.13618/j.issn.1001-5728.2024.S.039 . |
| CHEN D. Discussion on identification cases of iatrogenic cyanide accumulation and poisoning[J]. Zhongguo Fayixue Zazhi,2024,39(S1):75-76. | |
| [3] | HENDRY-HOFER T B, NG P C, WITEOF A E, et al. A review on ingested cyanide: Risks, clinical presentation, diagnostics, and treatment challenges[J]. J Med Toxicol,2019,15(2):128-133. doi:10.1007/s13181-018-0688-y . |
| [4] | OSAK M, BUSZEWICZ G, BAJ J, et al. Determination of cyanide in blood for forensic toxicology purposes — A novel NCI GC-MS/MS technique[J]. Molecules,2021,26(18):5638. doi:10.3390/molecules26185638 . |
| [5] | AKHGARI M, BAGHDADI F, KADKHODAEI A. Cyanide poisoning related deaths, a four-year experience and review of the literature[J]. Aust J Forensic Sci,2016,48(2):186-194. doi:10.1080/00450618.2015.1045552 . |
| [6] | 魏鑫,王遥雪,凌约涛,等. 顶空气相色谱法测定固体废物中氰化物[J].化学分析计量,2020,29(6):15-18. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2020.06.004 . |
| WEI X, WANG Y X, LING Y T, et al. Determination of cyanide in solid wastes by headspace gas chromatography[J]. Huaxue Fenxi Jiliang,2020,29(6):15-18. | |
| [7] | 左家信,范翔,李欣,等. 顶空-气相色谱法测定饮用水中的氰化物和氯化氰[J].分析仪器,2023(5):36-40. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-232x.2023.05.008 . |
| ZUO J X, FAN X, LI X, et al. Determination of cyanide and cyanogen chloride in drinking water by headspace-gas chromatography[J]. Fenxi Yiqi,2023(5):36-40. | |
| [8] | 温尚龙,陈欣义,庞兆东,等. 一种快速定性测试废水处理中氰化物含量的检测方法:CN112798577A[P].2021-05-14. |
| WEN S L, CHEN X Y, PANG Z D, et al. A rapid qualitative detection method for cyanide content in wastewater treatment: CN112798577A[P]. 2021-05-14. | |
| [9] | 王晓芳,陈美,杨春亮,等. 木薯中氰化物含量的异烟酸-吡唑林酮分光光度法测定[J].分析仪器,2009(1):32-34. |
| doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-232X.2009.01.010.WANG X F, CHEN M, YANG C L, et al. Determination of cyanide in cassava by isonicotinic acid-pyrazolone spectrophotometry[J]. Fenxi Yiqi,2009(1):32-34. | |
| [10] | WEI Y, TANG J, ZHANG J, et al. A label-free fluorescent-hydrogel sensor for heparin detection in diluted whole blood[J]. Chem Commun (Camb),2025,61(6):1215-1218. doi:10.1039/d4cc03780d . |
| [11] | YANG W, YE L, WU Y, et al. Arsenic field test kits based on solid-phase fluorescence filter effect induced by silver nanoparticle formation[J]. J Hazard Mater,2024,470:134038. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134038 . |
| [12] | JACKSON R, ODA R P, BHANDARI R K, et al. Development of a fluorescence-based sensor for rapid diagnosis of cyanide exposure[J]. Anal Chem,2014,86(3):1845-1852. doi:10.1021/ac403846s . |
| [13] | LIN Y, YE S, TIAN J, et al. Paper-assisted ratiometric fluorescent sensors for on-site sensing of sulfide based on the target-induced inner filter effect[J]. J Hazard Mater,2023,459:132201. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132201 . |
| [14] | LIN Y, LI Y, CHANG H, et al. Rapid testing of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and its metabolite on-site using a label-free ratiometric fluorescence assay on a smartphone[J]. Anal Chem,2023,95(18): 7363-7371. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.3c00666 . |
| [15] | ZHOU J, CHEN X, WEI Y, et al. Portable and rapid fluorescence turn-on detection of total pepsin in saliva based on strong electrostatic interactions[J]. Anal Chem,2023,95(49):18303-18308. doi:10. 1021/acs.analchem.3c04723 . |
| [16] | LONG L, YUAN X, CAO S, et al. Determination of cyanide in water and food samples using an efficient naphthalene-based ratiometric fluorescent probe[J]. ACS Omega,2019,4(6):10784-10790. doi:10.1021/acsomega.9b01308 . |
| [17] | HU Y, LU X, JIANG X, et al. Carbon dots and AuNCs co-doped electrospun membranes for ratiometric fluorescent determination of cyanide[J]. J Hazard Mater,2020,384:121368. doi:10.1016/j.jhaz mat.2019.121368 . |
| [18] | LIU Y, AI K, CHENG X, et al. Gold-nanocluster-based fluorescent sensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of cyanide in water[J]. Adv Funct Mater,2010,20(6):951-956. doi:10.1002/adfm.200902062 . |
| [19] | SUN Z, WU Z, ZONG Y, et al. Construction of metal-organic framework as a novel platform for ratiometric determination of cyanide[J]. Biosensors (Basel),2024,14(6):276. doi:10.3390/bios14060276 . |
| [20] | YANG H, YANG Y, LIU S, et al. Ratiometric and sensitive cyanide sensing using dual-emissive gold nanoclusters[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem,2020,412(23):5819-5826. doi:10.1007/s00216-020-02806-2 . |
| [21] | WEI Y, YANG L, YE Y, et al. A simple aptamer-dye fluorescence sensor for detecting Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and its metabolite in urban sewage[J]. Chem Commun (Camb),2024,60(39):5205-5208. doi:10.1039/d4cc00824c . |
| [22] | YE S, YU B, REN T, et al. Point-of-care platform based on solid-phase fluorescence filter effect for urinary iodine testing in children and pregnant women[J]. Anal Chem,2023,95(37):13949-13956. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02531 . |
| [23] | PAN W, HAN L, CAO X, et al. Dual-response near-infrared fluorescent probe for detecting cyanide and mitochondrial viscosity and its application in bioimaging[J]. Food Chem,2023,407:135163. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135163 . |
| [24] | PENG T, LI S, ZHOU Y, et al. Two cyanoethylene-based fluorescence probes for highly efficient cyanide detection and practical applications in drinking water and living cells[J]. Talanta,2021,234:122615. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122615 . |
| [25] | LI Q, NIE J, SHAN Y, et al. Water-soluble fluorescent probe for simultaneous detection of cyanide, hypochlorite and bisulfite at different emission wavelengths[J]. Anal Biochem,2020,591:113539. doi:10. 1016/j.ab.2019.113539 . |
| [26] | MAGESH K, VIJAY N, WU S P, et al. Dual-responsive benzo-hemicyanine-based fluorescent probe for detection of cyanide and hydrogen sulfide: Real-time application in identification of food spoilage[J]. J Agric Food Chem,2023,71(2):1190-1200. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c05567 . |
| [27] | MU S, GAO H, LI C, et al. A dual-response fluorescent probe for detection and bioimaging of hydrazine and cyanide with different fluorescence signals[J]. Talanta,2021,221:121606. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121606 . |
| [28] | KONGSANAN N, PIMSIN N, KEAWPROM C, et al. A fluorescence switching sensor for sensitive and selective detections of cyanide and ferricyanide using mercuric cation-graphene quantum dots[J]. ACS Omega,2021,6(22):14379-14393. doi:10.1021/acso mega.1c01242 . |
| [29] | OGUZ A, OGUZ M, KURSUNLU A N, et al. A fully water-soluble Calix[4]arene probe for fluorometric and colorimetric detection of toxic hydrosulfide and cyanide ions: Practicability in living cells and food samples[J]. Food Chem,2023,401:134132. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134132 . |
| [30] | ERDEMIR S, MALKONDU S. Visual and quantitative detection of CN- ion in aqueous media by an HBT-Br and thiazolium conjugated fluorometric and colorimetric probe: Real samples and useful applications[J]. Talanta,2021,221:121639. doi:10. 1016/j.talanta.2020.121639 . |
| [31] | SERT A, ERDEMIR S, MALKONDU S. Ratiometric detection and monitoring of cyanide in biological, environmental and food samples by a novel triphenylamine-xhantane based fluorescent probe[J]. Anal Chim Acta,2024,1320:343000. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2024.343000 . |
| [32] | MAJEED S, WASEEM M T, KHAN G S, et al. Development of AIEE active fluorescent and colorimetric probe for the solid, solution, and vapor phase detection of cyanide: Smartphone and food applications[J]. Analyst,2022,147(17):3885-3893. doi:10.1039/d2an00937d . |
| [33] | NG B, QUINETE N, GARDINALI P R. Assessing accuracy, precision and selectivity using quality controls for non-targeted analysis[J]. Sci Total Environ,2020,713:136568. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020. 136568 . |
| [1] | 高妍, 陈芳, 夏文涛, 杨小萍, 王泽宇, 杨泽人, 刘霞, 盛延良. Chirp ABR的研究进展及其在法医学听力鉴定中的应用展望[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 387-393. |
| [2] | 李文艳, 赵晋峰, 刘唯琛, 吕诗婧, 张佳欣, 张旭东, 尉志文, 贠克明, 张潮. 虫螨腈及其代谢物在大鼠体内的毒物代谢动力学[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 380-387. |
| [3] | 沈敏. 证据可靠性视角下的法医毒物学实践与思考[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 297-306. |
| [4] | 施妍. 快检技术赋能法医毒物学的实践与挑战[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 307-313. |
| [5] | 韦丽霞, 刘波, 杨小圆, 张茜, 兰艺凤, 张潮, 贾娟, 张丹, 尉志文, 贠克明, 陈哲. 基于核酸适配体功能化氧化石墨烯荧光传感器检测氯胺酮及去甲氯胺酮[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 326-339. |
| [6] | 李嘉豪, 凌江, 蔡子豪, 郑梓源, 丁艳君. 基于铜纳米酶和分子印迹技术的替来他明快速检测荧光探针开发[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 355-363. |
| [7] | 郭紫雯, 邱天禹, 曹玥. 基于表面增强拉曼光谱与机器学习的依托咪酯及其结构类似物的快速鉴识[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 364-370. |
| [8] | 唐梦瑶, 黄博宇, 刘翠梅, 刘雪燕, 贾薇, 花镇东. 基于便携式质谱仪的依托咪酯及其类似物的快速筛查[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 348-354. |
| [9] | 宝景春, 赵晶京, 李骄勇, 孟菁华, 王晓龙, 詹晓妮, 姚军, 吴旭. 法医从业者岗位胜任力评价模型的构建[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 371-379. |
| [10] | 田一鸣, 严一博, 文迪, 施妍. 新型功能材料在新精神活性物质快速检测中的研究进展[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 314-325. |
| [11] | 刘纤纤, 张涵, 张世宏. 苯中毒致再生障碍性贫血残疾等级评定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 289-291. |
| [12] | 廖琦, 刘永红, 焦英, 杨晓莹, 杨怡华, 刘翠梅, 高瑞霞. 台式低场核磁共振技术的发展及其在禁毒领域中的应用[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 267-276. |
| [13] | 刘冬梅, 朱英芝, 于凯丽, 陈捷敏, 刘良. 眶内眼球外异物致视神经损伤2例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 286-288. |
| [14] | 苏莉, 汪露, 钱起玥, 李倩倩, 杨丽, 胡永良. 凹陷型锁骨菱形窝用于胸片同一认定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 283-285. |
| [15] | 任申莉, 夏元飞. 交通事故外伤后颅内出血合并脑动静脉畸形损伤程度鉴定1例[J]. 法医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 291-293. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||